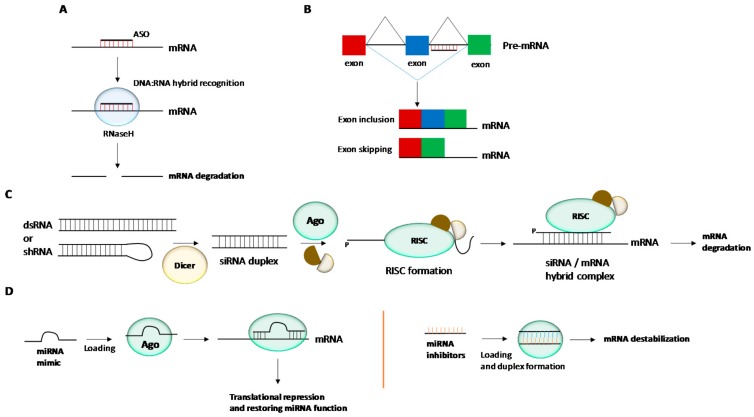
Figure 1.
Gene regulation mechanisms mediated by antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs), triplex-forming oligonucleotides (TFOs), small interference RNAs (siRNAs) and microRNAs (miRNAs). (A) Antisense technology: RNAseH is able to recognize DNA:RNA hybrid complexes which leads to mRNA degradation and the blockade of protein synthesis. (B) RNA splicing mechanisms in order to restore the disrupted reading fragment of a gene by using ASOs targeting intron and exon junctions. (C) RNA interference: The siRNA duplex is unwound and the guide strand is recognized by Ago2. The resultant RISC complex is able to interact with complementary sequence of a target mRNA. (D) MiRNA technology: Gene expression can be modulated by using double or single-stranded miRNA mimics in order to restore the miRNA function by inhibiting translation process. MiRNA inhibitors with complementary sequences to miRNAs can also be used for inactivating ncRNAs.