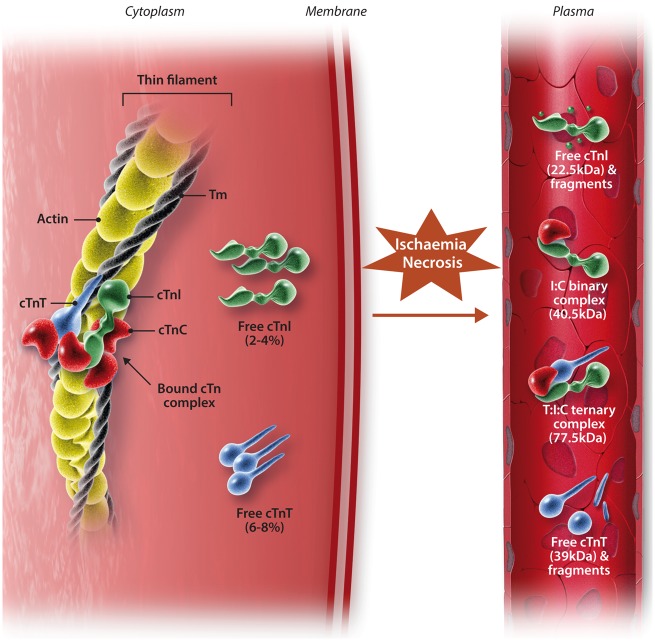
Figure 2.
Structure of the cardiac troponin-tropomyosin complex and the forms of troponin released following myocardial necrosis. Whilst most cardiac troponin (cTn) is bound to the myofibril, there is different subcellular localization of some cTn. ∼2–4% and ∼6–8% of cTnI and cTnT respectively exist either unbound in the cytosol, or loosely bound to the sarcomere. Following myocardial ischaemia, the ensuing necrosis of cardiac myocytes results in different forms of cTn being detectable in serum. After ischaemic insult, the free forms of cTnI and cTnT from the cytosol are soon detected in serum prior to detection of the complexed forms. There are several complexed forms that exist: non-covalent ternary complexed cTnT-I-C (T:I:C complex) and binary complexed cTnI-T (I:T complex). Edited from Gaze and Collinson34 with permission.