Figure 3.
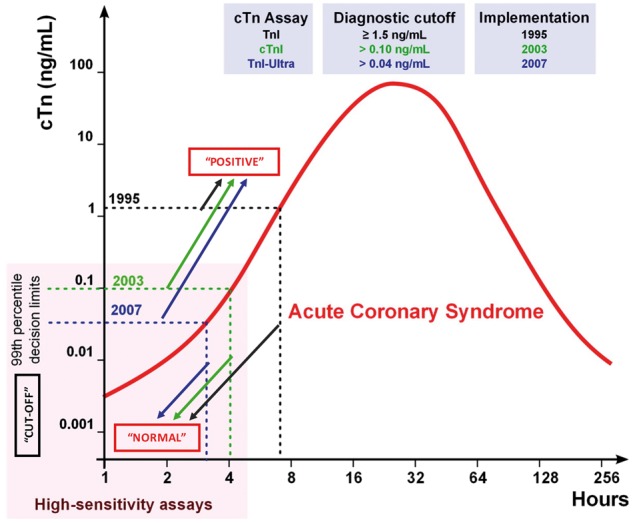
The 99th percentile diagnostic cut-off for cardiac troponin (cTn) assays. A hypothetical case of an acute coronary syndrome is shown to illustrate the evolution of cTn assay precision and sensitivity. The diagnostic cut-off for cTnI assays in 1995 was ≥ 1.5 ng/mL, in 2003 > 0.10 ng/mL and in 2007 > 0.04 ng/mL. The increasing sensitivity of the assays meant that very small concentrations of cTn could be detected, thus the 99th percentile decision limit had to be lowered. The 99th percentile quantitatively represents a value at which 1 person in 100 will have a false positive result.6 Any concentration of cTn detected within the 99th percentile decision limit suggests a ‘normal’ result. Any concentration value which falls outside this decision limit indicates a ‘positive’ cTn and substantiates a possible AMI. Edited from Mahajan and Jarolim87 with permission.
