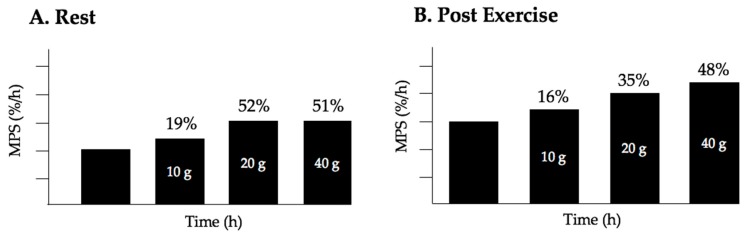
Figure 2.
Whey protein ingestion-induced increase in MPS in young men, percent change from 0 g. (A) At rest, consumption of 10 g or 20 g of protein results in a rise of 19% and 52% respectively from 0g. Consumption of 40 g of whey protein does not result in superior stimulation of MPS beyond consumption of 20 g; (B) Following resistance exercise, consumption of 20 g of protein increases MPS almost twice as much as consumption of 10 g, while consumption of 40 g of whey protein results in a small stimulation of MPS over and above that seen at 20 g indicating there are diminishing returns in terms of stimulation of MPS above 20 g. Data redrawn from Witard et al. [35], however, similar data are reported by MacNaughton et al. [38], and Moore et al. [36].