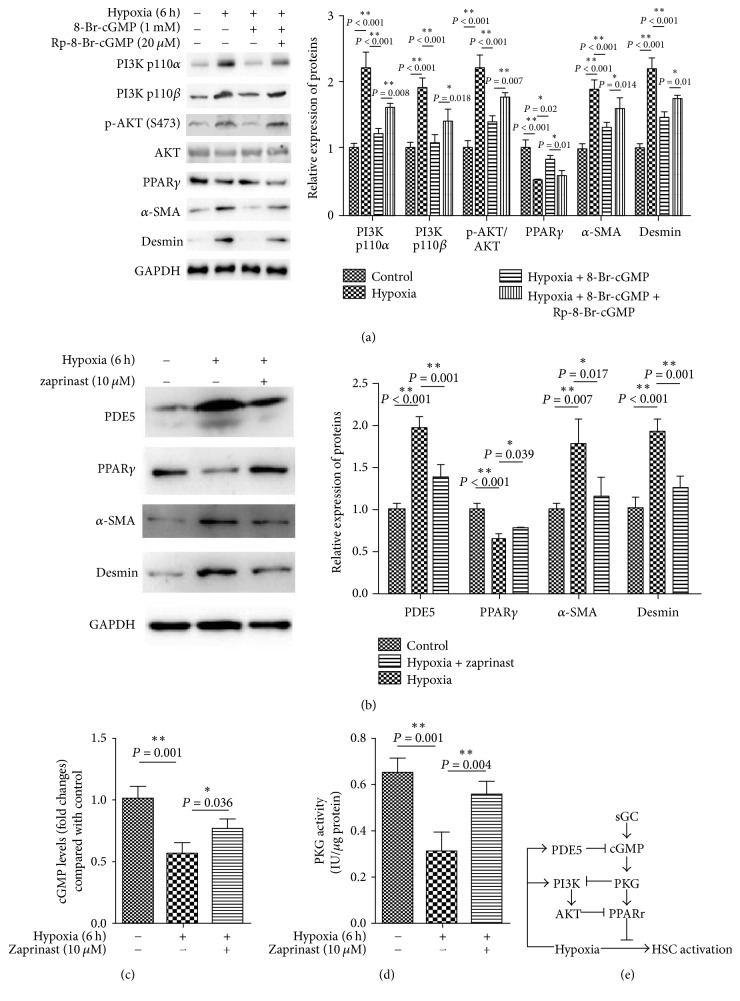
Figure 4.
sGC/cGMP/PKG and PI3K/AKT signals synergistically act on PPARγ to inhibit hypoxia-induced HSC activation. (a) HSCs were exposed to hypoxia in the presence of cGMP analog, 8-Br-cGMP (1 mM), or agonist, Rp-8-Br-cGMPs (20 μM). PI3K p100 α, p100β, phosphorylated AKT, total AKT, PPARγ, α-SMA, and desmin expression of HSCs in experimental groups were detected by western blotting. HSCs were exposed to hypoxia in the presence of PDE5 agonist, zaprinast (10 μM). (b) PDE5, PPARγ, α-SMA, and desmin expression of HSCs in experimental groups were measured by western blotting. (c)-(d) cGMP and PKG activity were tested, respectively. (e) Possible signal pathway involved in this study. Hypoxia induces HSCs activation. However, PPARγ inhibits this effect, which is triggered by sGC/cGMP/PKG signaling. Hypoxia promotes PI3K/AKT signaling and PDE5, which inhibit cGMP and PPARγ, respectively. Finally, sGC/cGMP/PKG and PI3K/AKT signals synergistically act on PPARγ to inhibit hypoxia-induced HSC activation. For each assay, n = 3. ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01.