Fig. 6.
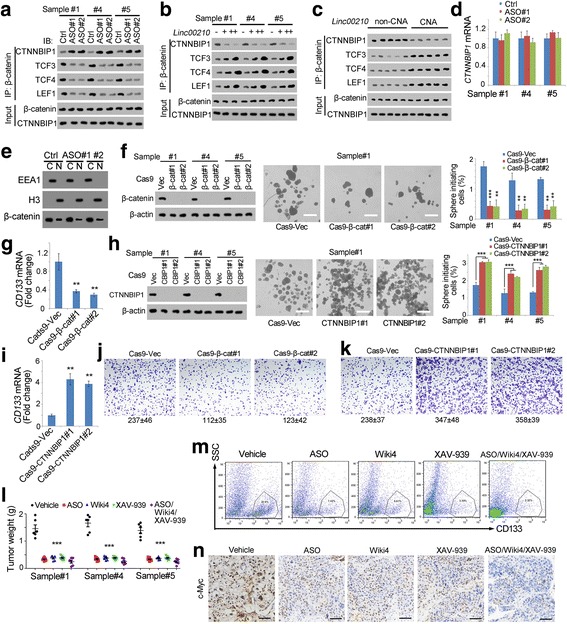
Linc00210-Wnt/β-catenin signaling served as a target for liver TIC elimination. a-c β-catenin interaction analyses using co-immunoprecipitation assays with β-catenin antibody. Linc00210 silenced cells (a), overexpression cells (b) and copy number gained samples (c) were crushed with RIPA lysis buffer, and incubated with β-catenin antibodies. The enrichment samples were analyzed using Western blot with the indicated antibodies. d CTNNBIP1 expression levels in linc00210 silenced cells were examined by realtime PCR. e Linc00210 silenced cells were performed with nucleocytoplasmic separation, and subcellular location of β-catenin was examined by Western blot. EEA1 and H3 were cytoplasmic and nuclear markers, respectively. f β-catenin knockout cells were established using CRISPR/Cas9 approach (left panels), followed by sphere formation assays for self-renewal analysis. Typical sphere images were shown in middle panels and liver TIC ratios were shown in right panels. g CD133 expression levels in β-catenin knockout cells were examined by realtime PCR. h, i CTNNBIP1 knockout cells were generated, followed by sphere formation (h) and CD133 examination (i). j, k Transwell assays were performed using β-catenin knockout (j) and CTNNBIP1 knockout (k) cells. Typical images and cell numbers (mean ± s.d.) were shown. l Liver TICs were injected into BALB/c nude mice, and tumors were treated with the indicated reagents every 2 days. One month later, tumors were collected and weighted. XAV-393 is an inhibitor for Wnt/β-catenin signaling. m The indicated treated tumors were collected and stained with CD133-PE, and CD133 positive cells were gated as shown. n Immunohistochemistry of with c-Myc using the indicated treated tumors. Scale bars, f, h, 500 μm; n, 50 μm. For d, f, g, h, i, l, data were shown as means±s.d. **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001 by two-tailed Student’s t test. Data are representative of four independent experiments
