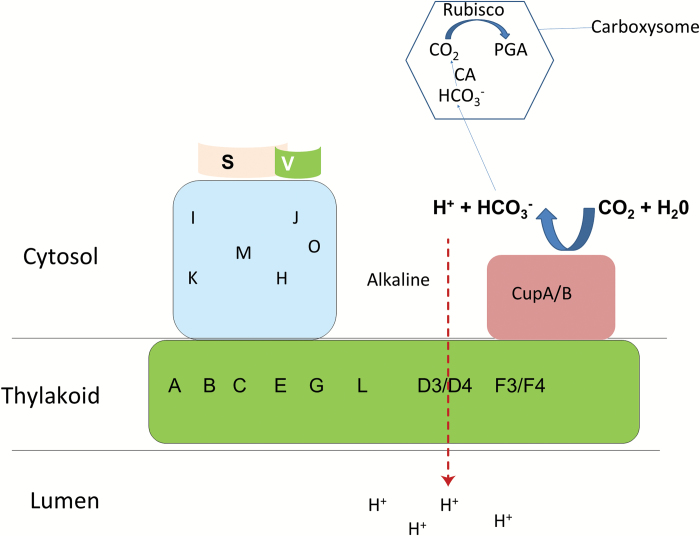
Fig. 5.
A model of the proposed function of CO2 uptake systems in Synechocystis sp. strain PCC6803. CupA or CupB converts CO2 into HCO3– under alkaline conditions, while the conversion is reversed under acidic conditions. Under light conditions, photosynthetic electron transfer couples to the formation of a transthylakoid membrane proton gradient, subsequently forming a strong alkaline region inside the U-type structure for CupA or CupB activity, which leads to the accumulation of HCO3– after CO2 has diffused into the cytosol. After HCO3– enters the carboxysome, it is converted into CO2 by CA for carbon assimilation by Rubisco. (This figure is available in color at JXB online.)