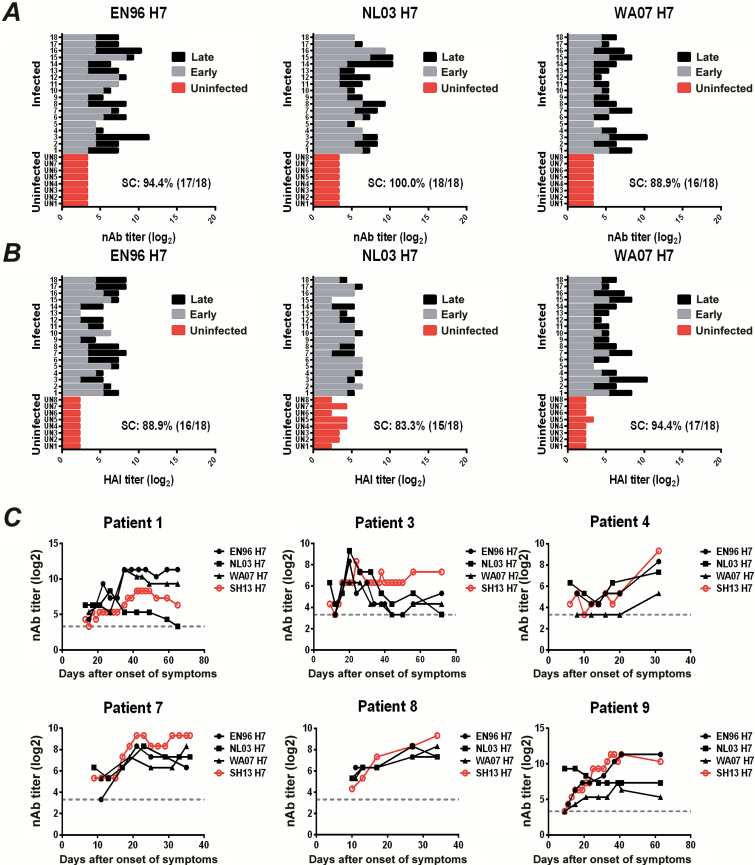
Figure 2.
Intrasubtypic antibody responses against heterologous H7 viruses in H7N9 infected patients. A, Neutralizing antibody (nAb) titers (log2) against EN96 H7 (left), NL03 H7 (middle), or WA07 H7 (right) pseudoviruses. B, Hemagglutination inhibition (HAI) titers (log2) against EN96 H7 (left), NL03 H7 (middle), or WA07 H7 (right) pseudoviruses. Serum samples from 18 H7N9-infected patients were collected at the early (gray) or late (dark) stages of infection as indicated above, and nAb or HAI titers were quantified using pseudovirus-based neutralization or HAI assays. Sera from 8 uninfected patients (red) were used as controls. The rate of seroconversion (SC) of HAI or nAb against pseudotyped viruses was defined as titers ≥40 or 4-fold increases. C, Dynamic nAb titers (log2) against EN96 H7 (●), NL03 H7 (■), or WA07 H7 (▲) were quantified in patients 1, 3, 4, 7, 8, and 9 using a pseudovirus-based assay. Dynamic nAb titers (log2) against homologous H7 virus SH13 H7 (red ○) were used as reference. The gray dashed line represents the geometric mean of the uninfected controls.