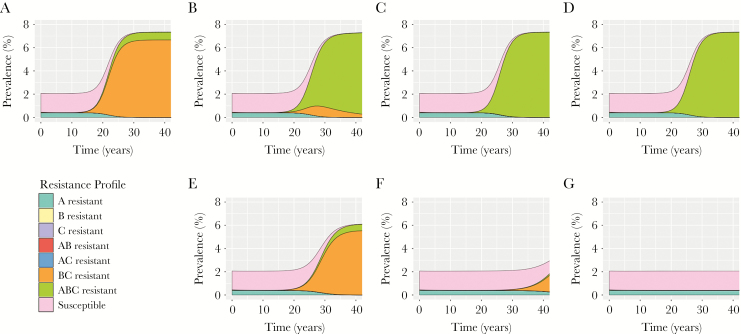
Figure 2.
Projected impact of point-of-care (POC) tests on gonorrhea prevalence and resistance. Population prevalence and prevalence of different strains are shown in the face of (A) no POC testing, (B and E) 10%, (C and F) 25%, and (D and G) 50% of cases tested. B–D show the results for a POC test for resistance to antibiotic A only. E–G show results for a POC test for resistance to all 3 antibiotics. For the 3-resistance POC test, cases undergoing testing and displaying susceptibility to >1 antibiotic were treated with the antibiotic with the highest fitness cost associated with resistance acquisition. For both scenarios, all untested cases were treated in combination with antibiotics B and C. Results are shown for tests with perfect sensitivity and specificity.