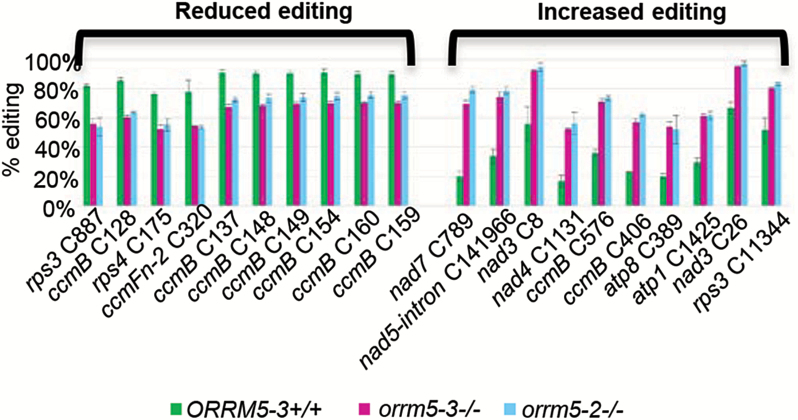
Fig. 2.
ORRM5 mutations cause mitochondrial editing defects. Ten sites that experienced a significant decrease of editing extent (Δ ≥10%) upon ORRM5 mutations (left), and ten sites that showed a significant increase of editing extent (Δ ≥10%) in the orrm5 mutants (right). ORRM5-3+/+, wild-type siblings of orrm5-3 mutants; orrm5-3–/–, orrm5-3 homozygous mutants; orrm5-2–/–, orrm5-2 homozygous mutants (n=2). Editing sites are displayed according to the difference between the wild-type and the mutants, from highest to lowest. Values represent mean±SD.