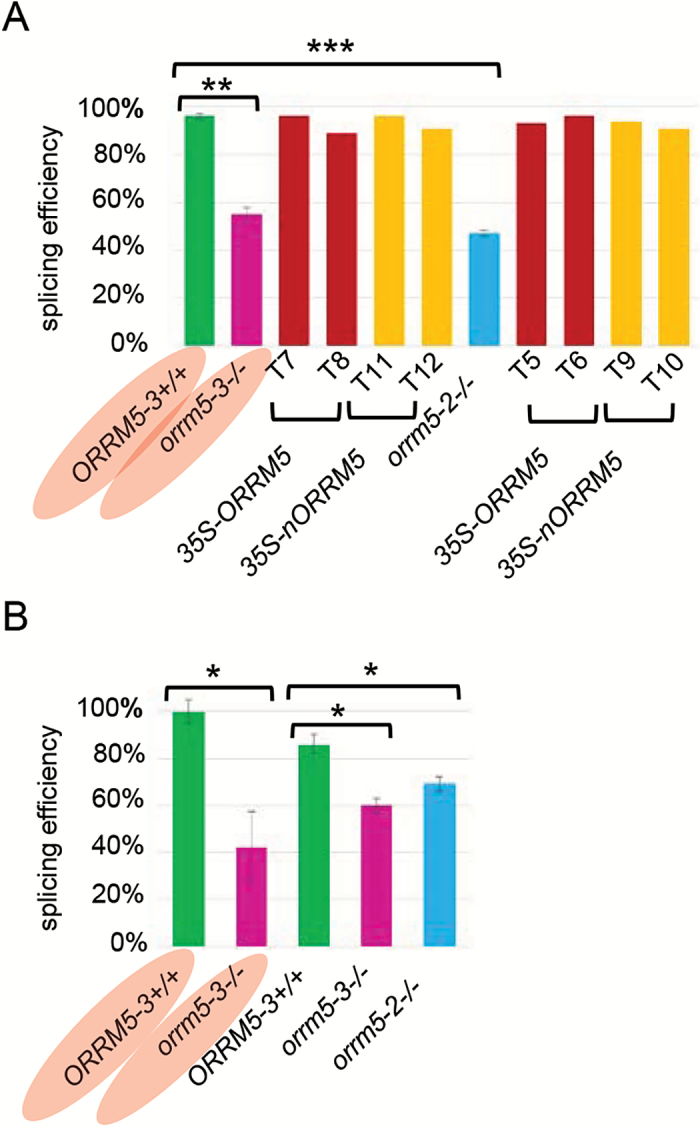
Fig. 7.
Cis-splicing of the first intron in the nad5 transcript is reduced in the orrm5 mutant plants. (A) Splicing efficiency was derived from the STS-PCRseq data by using ChloroSeq, a bioinformatic pipeline developed for chloroplast RNA-Seq. ORRM5-3+/+, wild-type siblings of orrm5-3 mutants; orrm5-3–/–, orrm5-3 homozygous mutants; T7 and T8, orrm5-3–/– w/35S:: ORRM5; T11 and T12, orrm5-3–/– w/35S:: nORRM5; T5 and T6, orrm5-2–/– w/35S:: ORRM5; T9 and T10, orrm5-2–/– w/35S:: nORRM5; 35S-ORRM5, mutant plants transformed with the coding sequence of ORRM5 under a 35S promoter; 35S-nORRM5, mutant plants transformed with the N-terminal RRM of ORRM5 under a 35S promoter. Values represent mean±SD for ORRM5-3+/+, orrm5-3–/–, and orrm5-2–/–. (B) Splicing efficiency was measured by qRT-PCR with three technical replications per sample. The same RNAs for the plants highlighted in red were tested by both methods. Student’s t-test: *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, n=2. Values represent mean±SD.