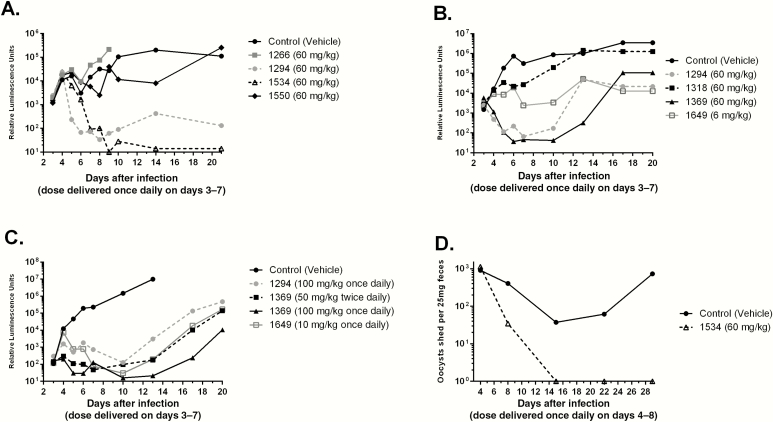
Figure 2.
Efficacy of bumped-kinase inhibitor (BKIs) in mouse models of Cryptosporidium parvum infection. A–C, Efficacies against C. parvum excretion in adult interferon γ knockout mice, based on nanoluciferase activity log RLU plotted on y-axis (A–C), and efficacy of BKI 1534 in SCID/beige mice, using reverse transcription–polymerase chain reaction to quantify infection (D). A, BKIs were delivered orally for 5 days, beginning 3 days after infection. In vivo inhibition by BKIs 1266, 1294, 1534, and 1550. BKI 1266, with limited inhibition of the C. parvum calcium-dependent protein kinase 1 target enzyme, was included as a negative control. BKIs 1294 and 1534 significantly reduced parasite shedding as compared to controls. The C. parvum infectious dose was 10000 oocysts. B and C, Significant initial reduction of parasite burden by BKIs, even in the case of higher fecal luciferase levels, which reflect higher parasites load. Parasite excretion rebounds when control animals show a higher infectious burden (B). BKIs 1294 (100 mg/kg once daily), 1369 (100 mg/kg once daily or 50 mg/kg twice daily), and 1649 (10 mg/kg once daily) efficacies (uninfected control mice had the highest recorded levels; C). BKIs substantially reduced Cryptosporidium proliferation, as shown by lower oocyst counts. A once-daily BKI 1369 dose of 100 mg/kg significantly reduced the infection burden (by 100000-fold), relative to that in untreated controls. BKI 1649 was administered at lower doses than other compounds owing to its high oral exposure, but it still significantly reduced infection relative to controls. The C. parvum infectious dose was 1000 oocysts. D, BKI 1534 delivered orally at a dose of 60 mg/kg for 5 days cleared infection with no recurrence. Assays were performed at the University of Georgia (Athens; A), the University of Washington (Seattle; B and C), and the University of Texas Medical Branch (Galveston; D). For assays with results in panels A and B, the percentage inhibition of infection, relative to that in controls, after treatment (day 10) was calculated for each compound as follows: 1294, 99.5%; 1534, 99.4%; and 1550, 59.7% (A); and 1294, 99.9%; 1318, 37.6%; 1369, 99.9%; and 1649, 98.9% (B). There were 3 mice in each experimental group.