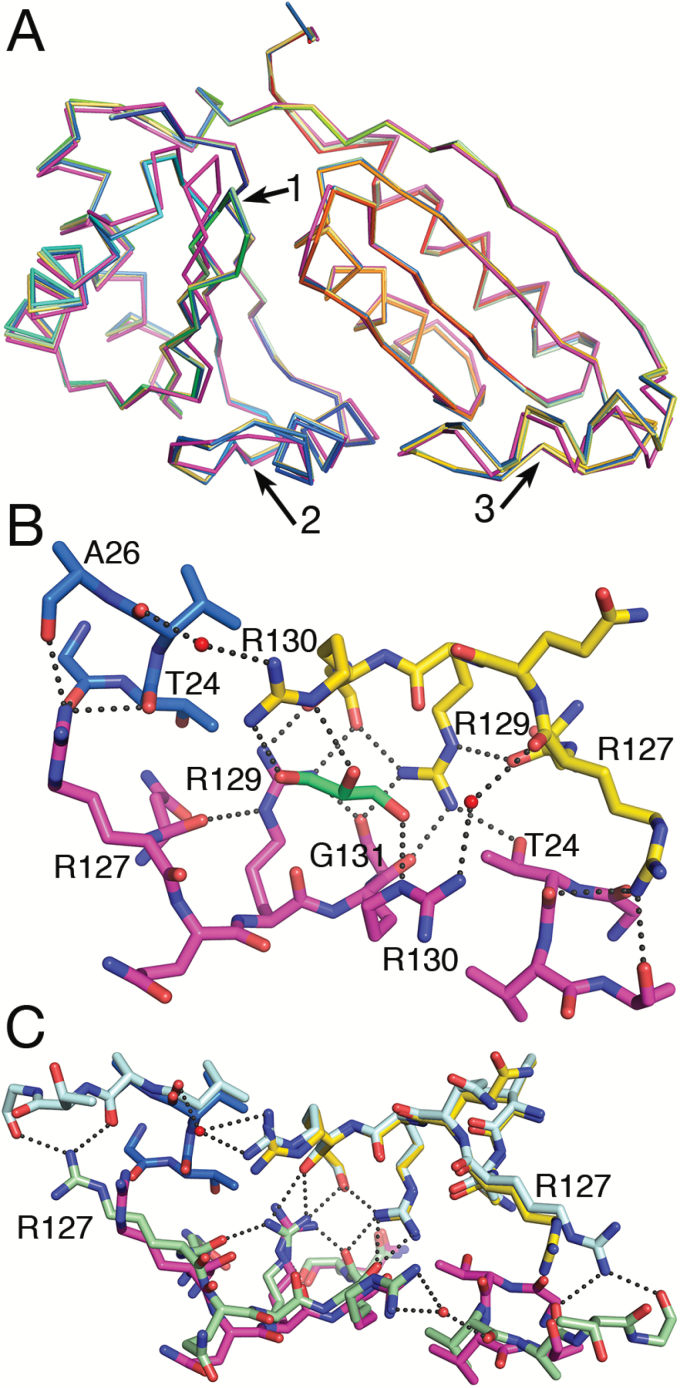
Fig. 4.
Interactions between monomers in the CcmP hexamer. (A) Differences in the SeCcmP main chain backbone in the open and closed conformation shown by superimposing SeCcmP_P213 monomer A (magenta) and monomer B (rainbow) and SeCcmP_I213 monomer B (yellow) and monomer C (green) on SeCcmP_I213 monomer A (blue). The only monomer with the gating residues in an open conformation is SeCcmP_P213 chain A (magenta). Structural deviations of the backbone in open and closed conformations are observed in the gating loops region (arrow 1), in helix α1 and the following loop region of the N-BMC domain (arrow 2) and in the corresponding helix α1'-loop region in the C-BMC domain (arrow 3). (B) Interactions in the helix–loop region between the two molecules in the asymmetric unit of SeCcmP_P213 (monomer A magenta and monomer B rainbow coloured). Salt bridges between Arg127 and Arg129 to backbone carbonyl groups and solvent form a rigid network of interactions that may mediate changes in the binding site of one trimeric ring to the binding site in the second ring. (C) SeCcmP_I213 monomer A (light blue) superimposed on SeCcmP_P213 chain B (rainbow coloured), and SeCcmP_I213 monomer C (green) superimposed on SeCcmP_P213 monomer A (magenta). Note the differences in salt bridges formed by the side chains of Arg127 in the two structures.