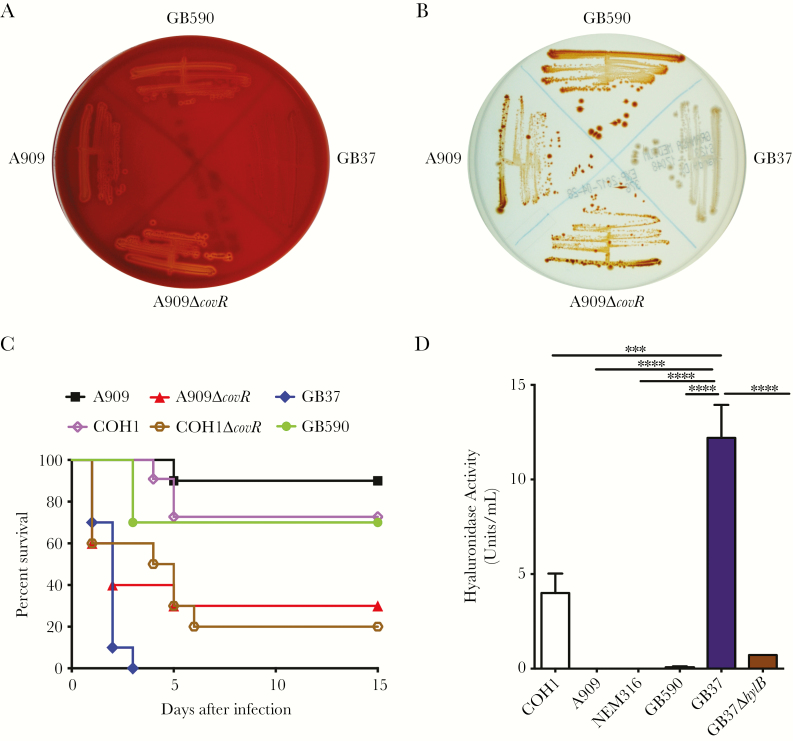
Figure 1.
GB37 exhibits decreased hemolysis and pigmentation but increased virulence and hyaluronidase activity. (A) The zone of clearing around the colonies on sheep blood agar indicates hemolytic activity. GB37 exhibits little-to-no hemolysis compared with GB590, A909, or A909ΔcovR. (B) Hemolytic group B streptococci (GBS) strains are pigmented, and nonhemolytic strains are nonpigmented on Granada Media. GB37 exhibits little-to-no pigmentation compared with GB590, A909, or A909ΔcovR. (C) Ten, 6- to 8-week-old wild-type (WT) C57BL/6J mice were given intravenous injections with 1 × 108 colony-forming units of GB37, GB590, A909, COH1, or hyperhemolytic strains (A909ΔcovR, COH1ΔcovR). Kalpan-Meier survival curve shows percentage survival of mice after the infection. Note that mice infected with GB37 succumbed to the infection within 4 days postinoculation in contrast those infected with A909, COH1, and GB590 (P < .0001, log-rank test), and GB37 virulence was similar to the ΔcovR strains. (D) Hyaluronidase activity of GB37 was compared with other GBS clinical isolates such as A909, COH1 NEM316, and GB590 and to GB37ΔhylB. Data shown represent the average of 3 independent experiments (error bars ± standard error of the mean). ***, P = .0004 and *****, P < .0001, Sidak’s multiple comparison test after analysis of variance.