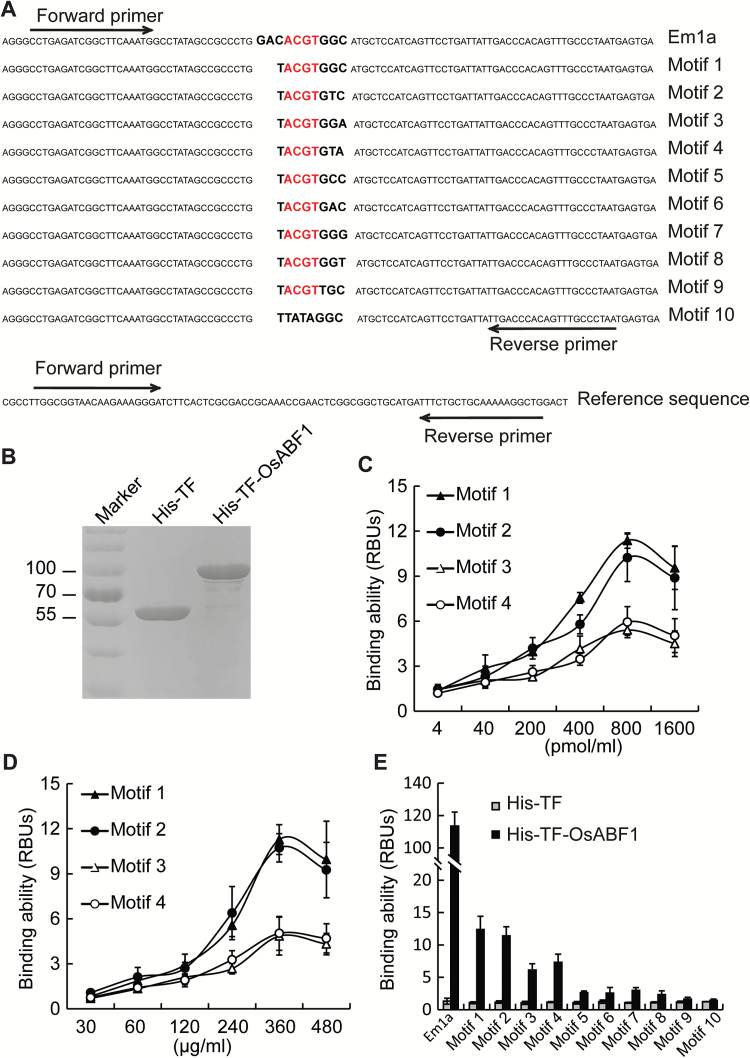
Fig. 3.
Quantitative PCR (qPCR)-based in vitro DNA binding assay. (A) DNA sequences containing the indicated motifs and an unrelated DNA sequence (reference sequence) used as an internal control are shown. Forward and reverse arrows indicate the primers used for qPCR. (B) The purified His-TF and His-TF-OsABF1 recombinant proteins were separated on an SDS-PAGE gel and stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue. His-TF indicates the His-tagged trigger factor chaperone, which facilitates co-translational folding of newly expressed polypeptides. (C) Binding ability of His-TF-OsABF1 to increasing concentrations of motif 1, 2, 3, or 4. The relative binding units (RBUs) were calculated using the formula: [RBU=2–△Ct, △Ct=Ct(Motif)–Ct(Reference); Ct (cycle threshold) represents the number of cycles required for the fluorescence signal to exceed the background level]. Mean values ±s.e.m. are shown (n=3). (D) Binding ability of each motif to increasing concentrations of His-TF-OsABF1 protein. RBUs were calculated as in (C). Mean values ±s.e.m. (standard error of the mean) are shown (n=3). € Binding ability of His-TF-OsABF1 to each motif. His-TF was used as a negative control.