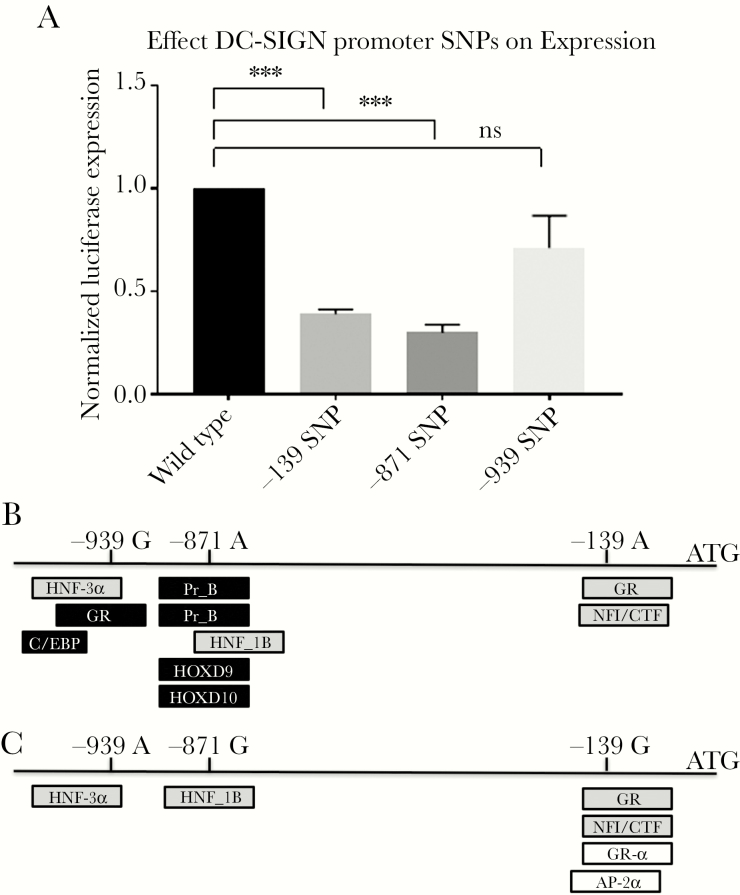
Figure 1.
Effect of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) on DC-SIGN promoter activity. A, The −139 SNP causes a reduction of 2.6 fold (P = .0005), the −871 SNP of 3.3 fold (P = .0009), and the −939 SNP a 1.4 fold (ns, not significant) (***P < 0.001). B, Protective SNPs affect transcription factor (TF) binding sites in the DC-SIGN promoter. Putative binding of TFs to DC-SIGN promoter sequences without (B ) and with (C ) protective SNPs. Some TFs do not bind anymore to the sequence containing protective SNPs (black), some bind both sequences (grey), and some bind exclusively to the SNP containing the protective variant (white).