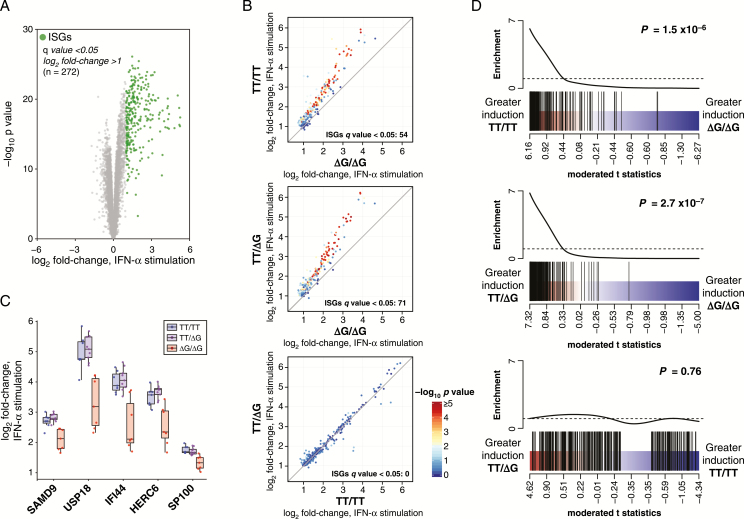
Figure 1.
Interferon-stimulated gene (ISG) fold-change induction is attenuated in chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) homozygous for ΔG/ΔG genotype at IFNL4 rs368234815 single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP). PBMC from individuals with chronic HCV were mock treated or stimulated with interferon-alpha (IFN-α) ex vivo and examined by RNA-Seq for gene expression fold-change analysis. A, Volcano plot depicting average fold-change in gene expression for PBMC samples (chronic HCV patients, n = 23) in response to IFN-α stimulation. PBMC IFN-stimulated gene (ISG) set (highlighted in green) was defined as q value < 0.05, log2 fold-change > 1, IFN-α stimulated versus unstimulated. B, PBMC ISG average fold-change expression (IFN-α simulated vs unstimulated) by IFNL4 rs368234815 SNP genotype (TT/TT, n = 7; TT/ΔG, n = 9; ΔG/ΔG, n = 7). Points are colored by –log10P value for indicated pairwise contrast. C, Individual sample fold-change expression (IFN-α simulated vs unstimulated) for the top 5 differentially induced ISGs in any pairwise contrasts (ranked by F test P value). D, Barcode plots representing PBMC ISG set enrichment in fold-change expression (IFN-α simulated vs unstimulated) by IFNL4 rs368234815 SNP genotype. PBMC ISGs (black bars) are ranked among all expressed genes by moderated t statistic for IFNL4 rs368234815 SNP genotype pairwise contrasts specified. P values for CAMERA gene set tests are indicated.