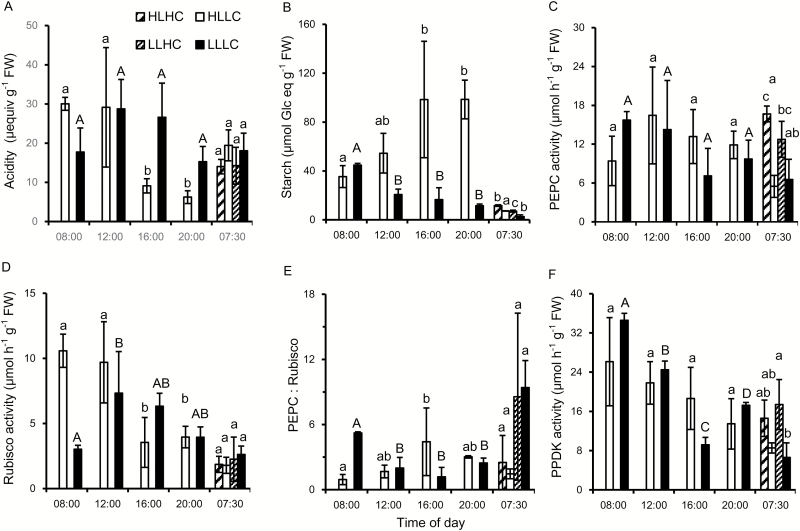
Fig. 5.
Effect of a short-term exposure to low light on diurnal changes in acidity, starch content, and enzyme activities in O. alismoides. Plants acclimated to high light (HL) and low CO2 (LC) were kept at low CO2 and exposed to low light (LLLC). At the end of the photoperiod, plants were treated overnight at high CO2 (HC) or kept at low CO2, and leaves were harvested at the end of the scotoperiod. (A) Acidity, (B) starch content as glucose equivalents, (C) PEPC activity, (D) Rubisco activity, (E) the PEPC:Rubisco ratio, and (F) PPDK activity. Bars show the mean with 1 SD for three replicates. Data with different letters are significantly different within a specific treatment. At the end of the scotoperiod (07.30 h), different letters designate treatments whose results are significantly different (P<0.05; one-way ANOVA).