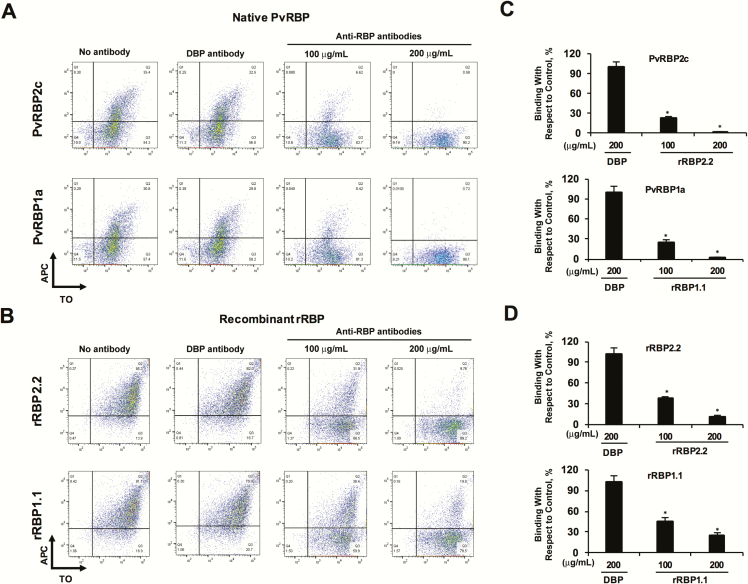
Figure 7.
Purified Plasmodium vivax reticulocyte-binding protein (PvRBP)–specific human antibodies block reticulocyte binding of the native and recombinant PvRBPs. A, B, Flow cytometry dot plots depicting the inhibition of binding of native PvRBP parasite (A) proteins and rRBP2.2/rRBP1.1 (B) proteins in the presence of the respective anti-PvRBP2c/anti-PvRBP1a human immunoglobulin G (IgG; 100 and 200 µg/mL, respectively). APC, allophycocyanin; TO, thiazole orange. C, D, Bar charts showing the percentage inhibition of reticulocyte binding of native PvRBPs (C) and rRBPs (D) by the anti-PvRBP/P. vivax Duffy-binding protein (PvDBP) IgG compared with binding in the absence of IgG. The reticulocyte binding of the native PvRBP2c/PvRBP1a and recombinant rRBP2.2/rRBP1.1 were potently blocked by the respective PvRBP2c/PvRBP1a-specific human IgGs. As controls, reticulocyte binding of PvRBP2c/PvRBP1a was analyzed in the presence of PvDBP-specific purified human antibodies. Anti-PvDBP human IgG failed to block the reticulocyte binding of native PvRBP2c and PvRBP1a proteins. Reticulocytes were enriched by magnetic sorting. *P < .001. Abbreviation: rRBP, recombinant RBP.