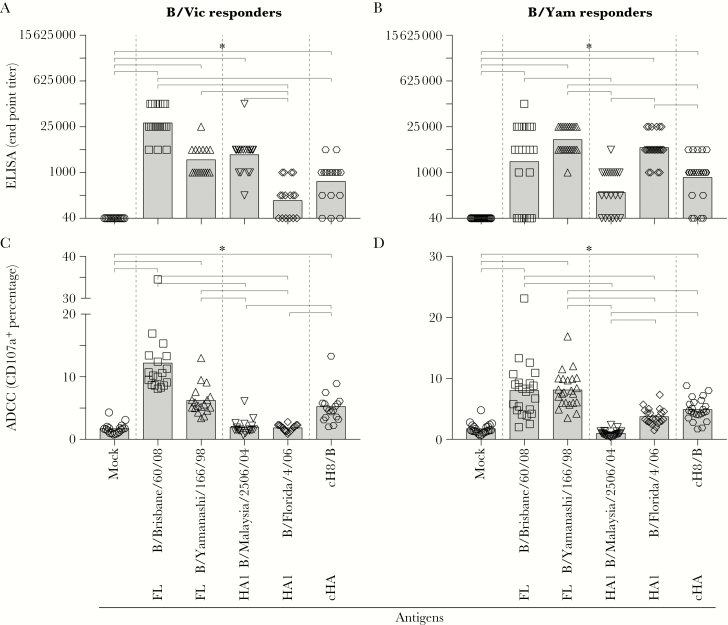
Figure 4.
Detection of antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity [ADCC]–mediating hemagglutinin (HA) stalk–specific and HA head–specific antibodies after primary influenza B virus (IBV) infection. A and B, Antibodies against either the full-length (FL) HA of both lineages, the HA1 of both lineages, or the HA stalk (cHA, chimeric HA) after a primary IBV infection were detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). End point titers were determined by creating 5-fold serial dilutions of serum samples, and a cutoff (end point) for the presence of specific antibodies was set at 3 times the background level. Statistically significantly higher end point titers were detected against the full-length HA of both lineages, the homologous HA1 subunit, and the HA stalk as compared to the phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) control. C and D, Presence of ADCC-mediating antibodies against either the full-length HA of both lineages, the HA1 of both lineages, or the HA stalk after a primary IBV infection. Statistically significantly higher CD107a+ were detected upon stimulation with the full-length HA of both lineages and the HA stalk as compared to the PBS control. Stimulation with the HA1 subunit only, homologous or heterologous, did not lead to significant differences as compared to the PBS control. A nonparametric Friedman test on paired samples with multiple comparisons was performed to compare the ELISA and ADCC data obtained with the different antigens.