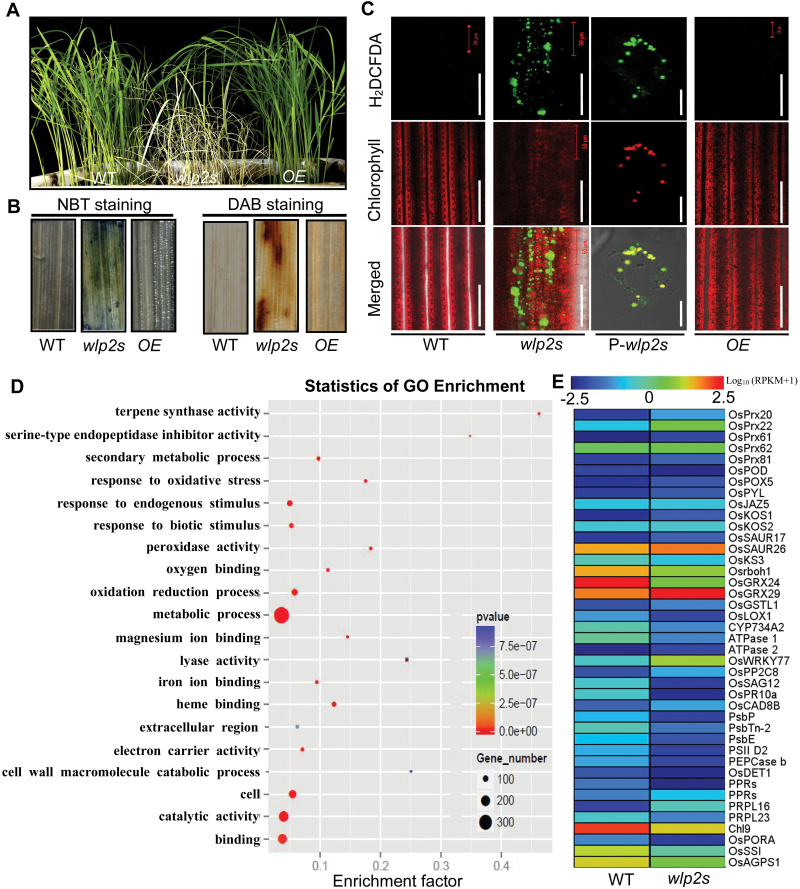
Fig. 7.
The wlp2 mutants showed heat-stress-induced death with elevated ROS accumulation. (A) Phenotype of wild-type (WT) and wlp2s plants at the four-leaf stage grown under heat stress (32 °C). (B) NBT and DAB staining in blades of 2-week-old seedlings in WT, wlp2s, and a WLP2 overexpression line (OE) grown at 32 °C. (C) Microscopic analysis of leaves of 2-week-old seedlings of WT, wlp2s, and WLP2 OE lines, and protoplast cells of wlp2s (P-wlp2s), incubated with H2DCFDA at 32 °C. Green staining represents oxidized H2DCFDA and red represents chlorophyll. H2DCFDA foci co-localize with chloroplasts in P-wlp2s. Bars=50 μm in WT, wlp2s, OE; bar=2 μm in P-wlp2s. (D, E) RNA-seq analysis of wlp2s and WT grown under the heat stress (32 °C) condition. (D) GO enrichment analysis of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between wlp2s and WT (P≤0.05). (E) Expression heat map of selected DEGs.