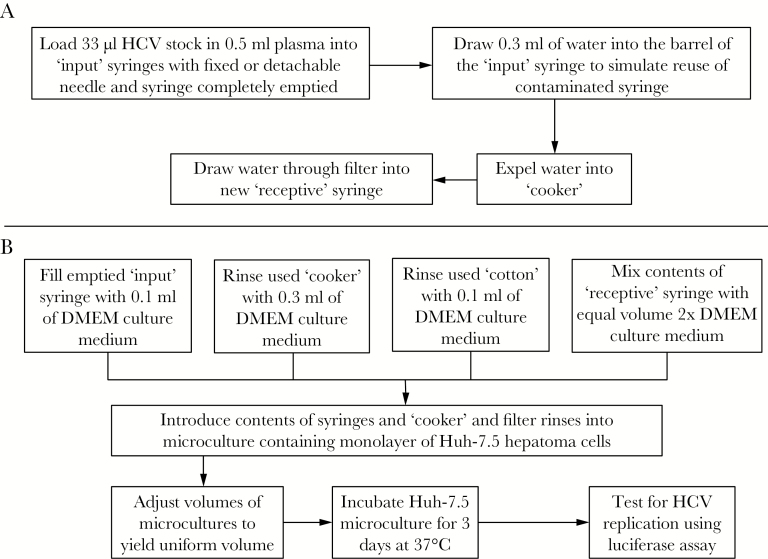
Figure 1.
Flow diagram of experiments to determine the recovery of infectious hepatitis C virus (HCV) from drug preparation and injection paraphernalia. (A) The process of producing the syringes and paraphernalia tested in this study is depicted, starting with syringes contaminated with HCV replicating the situation when a syringe previously used by an individual actively infected with HCV is then used to add water to dissolve drugs for injection. The water from the “input” syringes is then passed through a “cooker” and filter and into a “receptive” syringe. (B) The process for testing for potentially infectious HCV in each of the drug preparation and injection items is depicted. The volume of liquid tested is made uniform for all 4 items, and HCV replication after 3 days in microculture is measured according to the procedure described in the Methods and in Paintsil et al [30]. Abbreviation: DMEM, Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium.