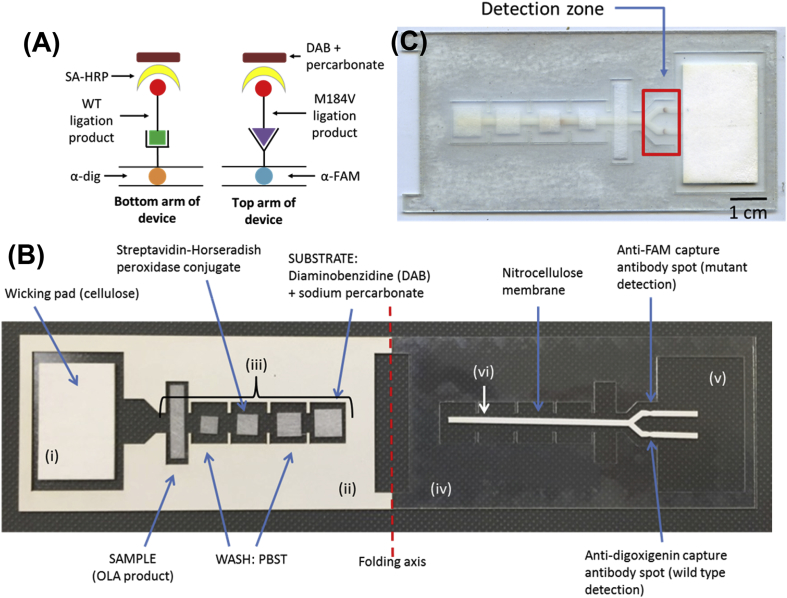
Fig. 3.
Lateral flow ELISA design. (A) A side view of the detection zone of the ELISA format for this lateral flow assay. OLA products are captured and detected by an enzyme-substrate mechanism. (B) Image of the lateral flow ELISA to discriminate HIV-1 mutant and wild type OLA products. After reagents are added, the adhesive backing on the left is removed and the device is folded and sealed along the folding axis to initiate flow and sequential delivery of reagents. The device parts indicated are: (i) cellulose wicking pad; (ii) adhesive acetate (paper side up); (iii) glass fiber pads; (iv) acetate; (v) adhesive acetate (paper backing removed and adhesive side up); (vi) nitrocellulose. (C) Image of the lateral flow design once folded. Starting with the OLA product contained in the glass fiber pad closest to the wicking pad, reagents flow sequentially across the detection zone.