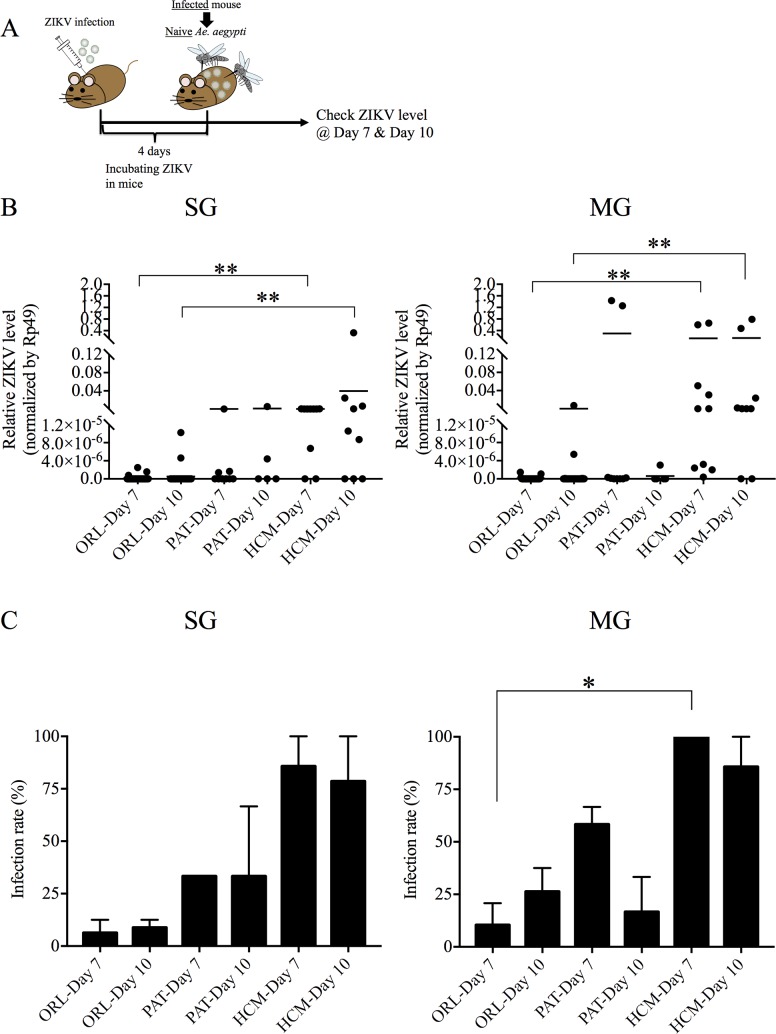
Fig 4. Vector capacity of ZIKV in Ho Chi Minh (HCM), Patilas (PAT) and Orlando (ORL) strains of Ae. aegypti, after taking a blood meal on mice.
HCM, PAT and ORL strains of Ae. aegypti were infected with ZIKV by allowing mosquitoes to ingest a blood meal from mice infected with ZIKV. (A) Experimental workflow for the ZIKV oral infection experiments. (B) ZIKV levels by qRT-PCR of the salivary glands (SG) and midgut (MG) of ORL, PAT and HCM mosquitoes 7 or 10 days after infection. ZIKV RNA levels were normalized to mosquito Rp49 RNA levels. (C) Infection rate of each strain infected at 7 and 10 days was calculated by comparing infected vs. uninfected mosquitoes in each experiment. Data shown are pooled from at least two independent experiments. (n = 35/group for ORL-Day 7; n = 28/group for ORL-Day 10; n = 8/group for PAT-Day 7; n = 5/group for PAT-Day 10; n = 10/group for HCM-Day 7; n = 9/group for HCM-Day 10.) Each data point represents an individual mosquito. Significance was calculated using one-way ANOVA. * P<0.05, ** P<0.01.