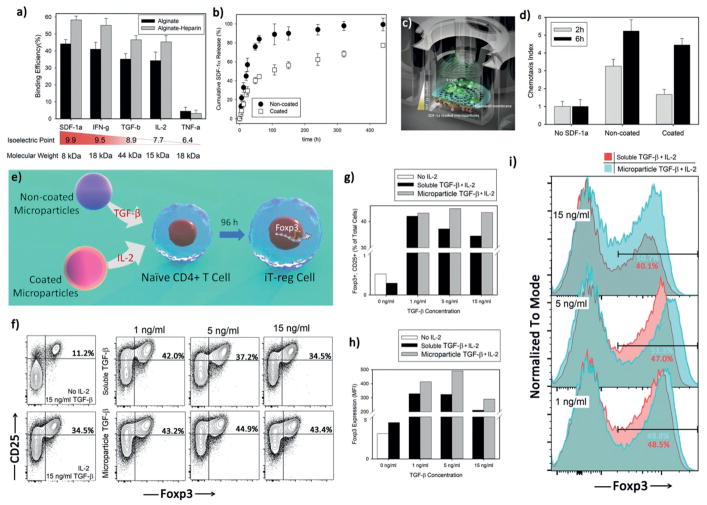
Figure 4.
Engineered microparticles can deliver other signals beside IL-2. a) Binding capacity of alginate-heparin microparticles was evaluated after incubating them with various cytokines at constant concentration of 50 ng mL−1 for 12 h at 4 °C and under continuous, gentle shaking. b) Release profile of SDF-1α cytokine from noncoated Alg-Hep microparticles at 37 °C. SDF-1α releasing microparticles (in the bottom of the well) generate a sustained gradient to recruit local T-cells as schematically illustrated in (c). d) Quantification of relative T-cell’s migration (chemotactic index) for active T-cells after 2 h of coculture with noncoated Alg-Hep microparticles at different initial loadings. The presented data are expressed as average ± SD. e) Sustained release of TGF-β mediates development of induced regulatory T-cells (iT-reg cells). f–i) Flow cytometric analysis of iT-reg development was assessed and judged by Foxp3 and CD25 coexpression after coculture of naïve CD4+ T-cells with anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 for 4 d. The indicated range of TGF-β concentrations was applied either in a soluble format or via noncoated microparticles at the same time as activation signal. All the samples contained IL-2 releasing coated microparticles that delivered 20 U mL−1 IL-2 during treatment. Control experiments (f) left panels) were also performed to show the effect of IL-2 presence in the constant concentration of TGF-β (15 ng mL−1).