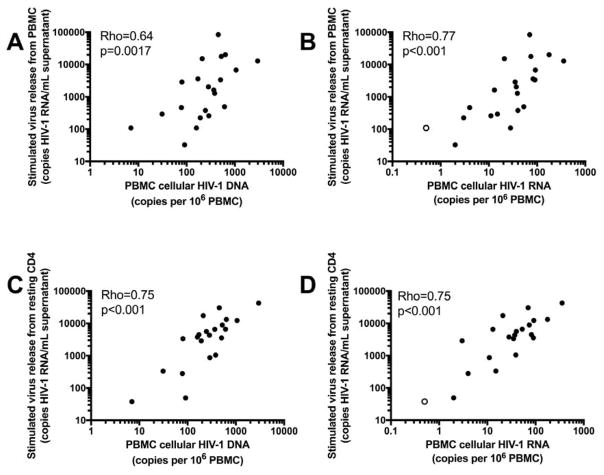
Fig. 5. The frequency of infected cells and their transcriptional activity in PBMC are correlated with the level of inducible virion release from PBMC and resting CD4+T-cells.
(a) The frequency of infected cells in PBMC is correlated with the level of inducible virion release from cultured PBMC treated with PMA/iono for 5 days (rho=0.64, p=0.0017). (b) The level of cellular unspliced HIV-1 RNA transcription is correlated with the level of inducible virion release from cultured PBMC (rho=0.77, p<0.001). (c) The frequency of infected cells in PBMC was correlated with the level of inducible virion release from cultured resting CD4+T-cells treated with PMA/iono for 7 days (rho=0.75, p<0.001). (d) The level of cellular unspliced HIV-1 RNA in PBMC is correlated with the level of inducible virion release from resting CD4+T-cells stimulated with PMA/iono (rho=0.75, p<0.001). In (b) and (d), one sample (shown as an open circle) had undetectable levels of cellular unspliced HIV-1 RNA. The value of this sample was interpolated as 50% of the limit of detection of the assay, or 0.5 copies per million PBMC.