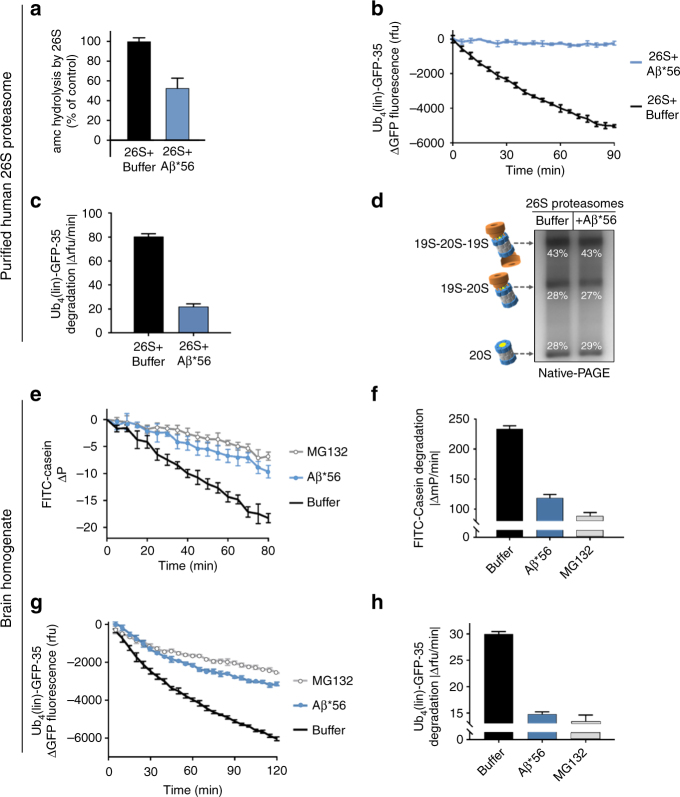
Fig. 5.
Aβ*56 oligomers inhibit ubiquitin-dependent and ubiquitin-independent degradation of full-length proteins. a–d Purified human 26S proteasomes. a Human 26S proteasome activity (LLVY-amc hydrolysis, rfu/min) with 2 μM Aβ*56 compared to buffer control. b Change in fluorescence of polyubiquitin-GFP fusion protein (Ub4(lin)-GFP-35) in the presence purified human 26S proteasome, with and without 5 μM Aβ*56. c Rate of polyubiquitin-GFP fusion protein (Ub4(lin)-GFP-35) degradation in c (Δrfu/min). d Purified human 26S proteasomes were incubated with or without Aβ*56 for 90 min at 37 °C, and separated by Native-PAGE and silver stained. Band density was quantified with ImageJ. Band density is shown as a percentage of total density of each lane. e–h Full-length protein degradation in mouse brain lysates. e Change in polarization of FITC labeled-casein in 2 μg mouse brain lysates, with and without 10 μM Aβ*56. f Rate of FITC-casein degradation in e (ΔmP/min). g Change in fluorescence of polyubiquitin-GFP fusion protein (Ub4(lin)-GFP-35) in 2 μg mouse brain lysates, with and without 10 μM Aβ*56. h Rate of polyubiquitin-GFP fusion protein (Ub4(lin)-GFP-35) degradation in g (Δrfu/min). The concentration of Aβ*56 oligomers is calculated based on Aβ monomeric peptide mass (4.5 kDa). All controls contained an equal volume of buffer identical to that of the Aβ*56 oligomers. The data are representative of three or more independent experiments performed in triplicate. Error bars represent ± standard deviation