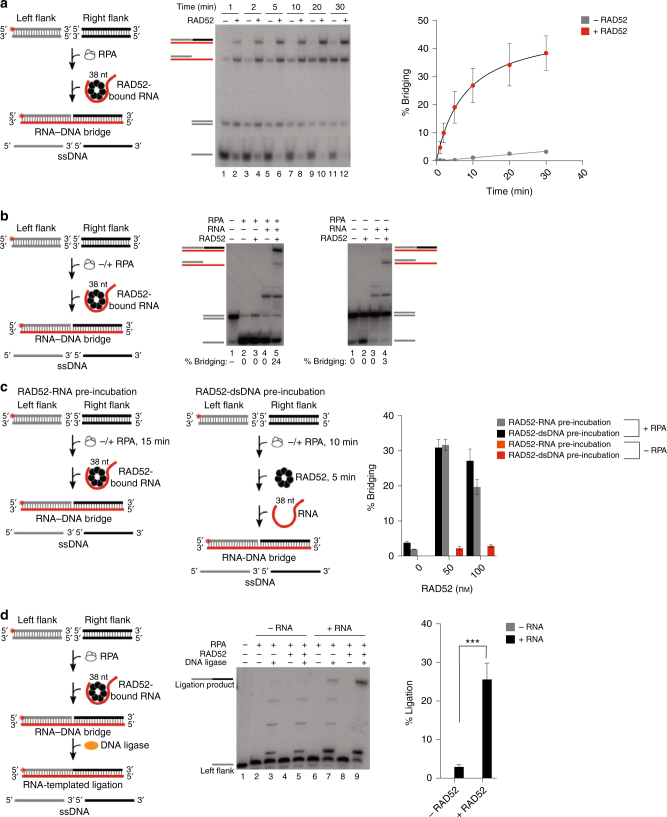
Fig. 4.
RAD52 promotes RNA-dependent recombinational repair of DSBs. a Schematic of assay (left). Non-denaturing gel showing a time course of RAD52-dependent RNA−DNA recombination (bridging) of blunt-ended DNA in the presence of RPA (middle). Plot showing time course of RAD52-dependent RNA−DNA recombination (bridging) of blunt-ended DNA in the presence of RPA (right). Data shown as average ± SEM, n = 3. b Schematic of assay (left). Non-denaturing gels showing RAD52-dependent RNA−DNA recombination (bridging) of blunt-ended DNA in the presence (left) and absence (right) of RPA. c Schematic of assays showing RAD52-dependent RNA−DNA recombination (bridging) of blunt-ended DNA employing either RAD52-dsDNA pre-incubation (right schematic) or RAD52-RNA (left schematic) pre-incubation steps, and performed either with and without RPA. Graph showing quantification of RAD52-dependent RNA−DNA recombination (bridging) of blunt-ended DNA utilizing the indicated pre-incubation steps and with and without RPA (right). Data shown as average ± SD, n = 3. d Schematic of assay (left). Denaturing gel showing RAD52-dependent RNA−DNA recombinational repair (bridging followed by ligation) of blunt-ended DNA in the presence of the indicated proteins and substrates (middle). Graph showing percent of RAD52-dependent RNA-mediated recombinational repair of blunt-ended DNA (% ligation) (right). Data shown as average ± SD, n = 3. ***, p = 0.0008 (unpaired Student’s t-test). * = 32P label