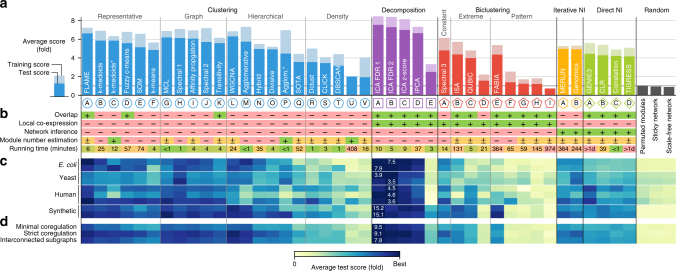
Fig. 2.
Overall performance of 42 module detection methods (Table 1) based on the agreement between observed modules and known modules in gene regulatory networks. The methods can be divided in five categories: clustering, decomposition, biclustering, direct network inference (direct NI) and iterative network inference (iterative NI) methods. Clustering and biclustering methods were further classified in subcategories (see Methods). a Average test and training scores across datasets and module definitions. The score represents a fold improvement over permutations of the known modules. *Automatic estimation of number of modules. b Different properties of the module detection methods (see Supplementary Note 2). A+ (green background) denotes that a method can handle a certain property listed on the left. We distinguish between explicit (−), implicit (±), and automatic (+) module number estimation. Note that running times strongly depend on the implementation, hardware, dataset dimensions, and parameter settings, and are therefore only indicative. c Test scores at each of the four datasets, averaged over module definitions. d Test scores on each of the three module definitions, averaged over different datasets