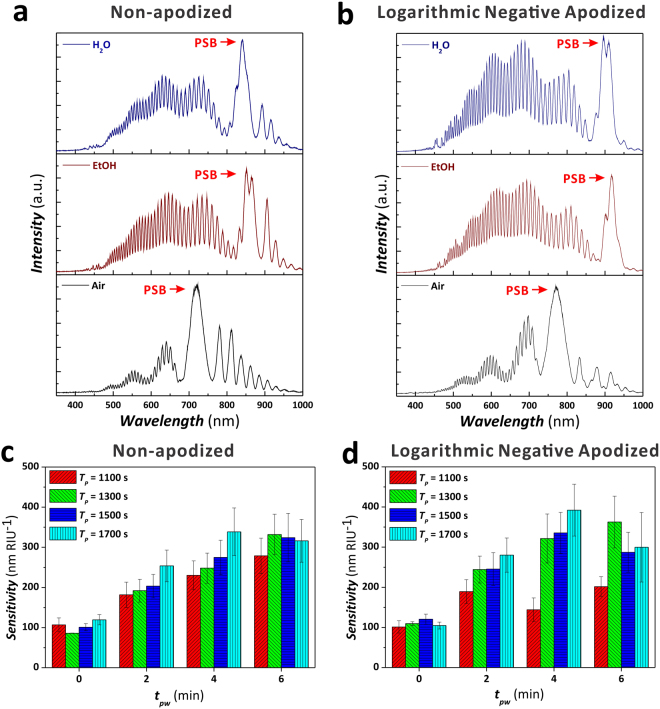
Figure 9.
Assessment of sensitivity of NAA-DBRs upon effective medium changes in non-apodized and apodized NAA-DBRs. (a) Representative RIfS spectra of a non-apodized NAA-DBR under different nanopores-infiltrating medium (i.e. air, ethanol, and water) (TP = 1700 s, AJ = 0.420 mA cm−2, Jmin = Joffset = 0.280 mA cm−2, tSTPA = 20 h, and tpw = 4 min). (b) Representative RIfS spectra of a logarithmic negative apodized NAA-DBR under different nanopores-infiltrating medium (i.e. air, ethanol, and water) (TP = 1700 s, ΔAJ = 0.210 mA cm−2, Jmin = Joffset = 0.280 mA cm−2, tASTPA = 20 h, and tpw = 4 min). (c) Bar chart showing the sensitivity in nm RIU−1 of non-apodized NAA-DBRs produced at different TP (1100, 1300, 1500, and 1700 s) and tpw (0, 2, 4, and 6 min) (AJ = 0.420 mA cm−2, Jmin = Joffset = 0.280 mA cm−2, and tSTPA = 20 h). (d) Bar chart showing the sensitivity in nm RIU−1 of logarithmic negative apodized NAA-DBRs produced at different TP (1100, 1300, 1500, and 1700 s) and tpw (0, 2, 4, and 6 min) (ΔAJ = 0.210 mA cm−2, Jmin = Joffset = 0.280 mA cm−2, and tASTPA = 20 h).