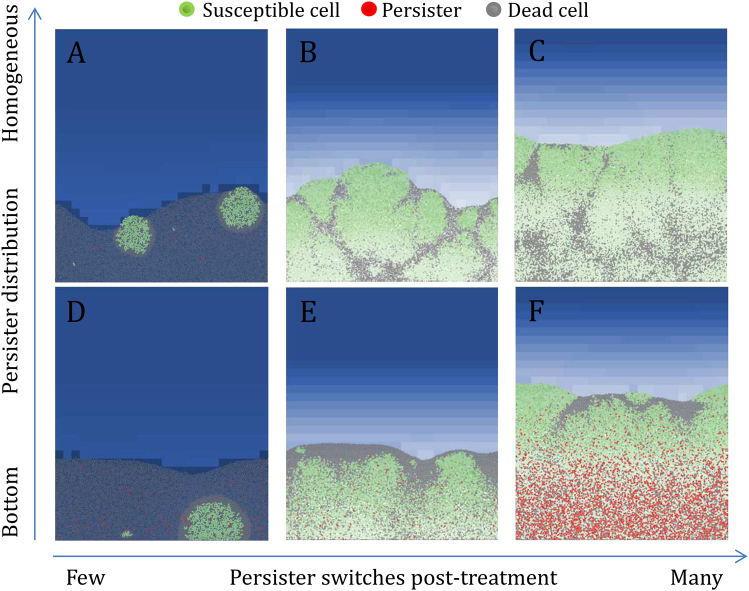
Fig. 5.
Structural patterns of the recovered biofilms 5 h after the treatment. The efficiency of the recovery depends on the number of persisters that have been able to switch to actively growing cells at the end of the treatment. This event depends on the number of persisters able to survive the treatment and on their switching rate b. A high rate of persister switches post-treatment leads to a fast recovery and thick biofilms after the 5 h of recovery. With the substrate-dependent strategy, persisters are mainly formed in substrate-deprived zones at the bottom of the biofilms. When persisters wake up at the bottom of the biofilms, the resulting colonies push against dead cells above them and form a shell of dead cells above the biofilms (d, e, f). With the constant and antibiotic-dependent strategies, persisters are homogeneously distributed in the biofilms. When persisters wake up randomly in the biofilms, the colonies push against dead cells around them and two colonies that encounter each other form characteristic strips of dead cells (a, b, c)