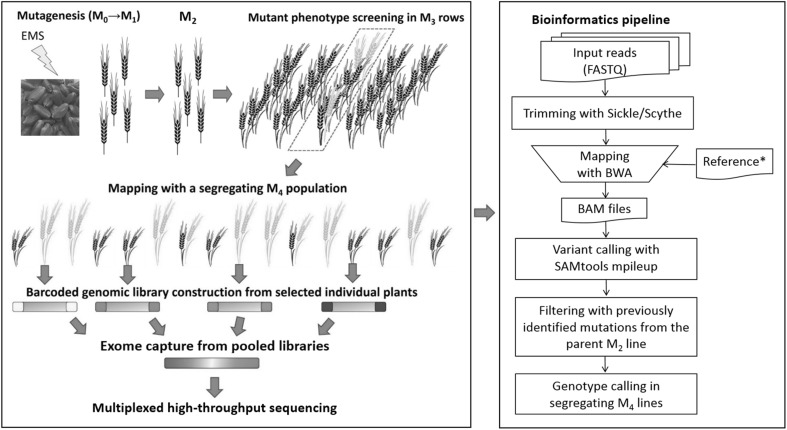
Fig. 2.
Overview of mutant mapping strategy using exome capture and sequencing. Each M1 plant grown from EMS-mutagenized seed was self-pollinated to produce single M2 plants, which were exome-sequenced to catalog induced mutations in the protein-coding regions (Krasileva et al. 2017). M3 rows derived from each M2 plant were screened to identify mutant phenotypes of interest (depicted in yellow). Subsequent M4 seeds bulk-harvested from the selected M3 row segregating for the mutant phenotype (red dotted box) were used as a mapping population. Barcoded sequencing libraries with unique indices were constructed for each of the selected individual M4 plants. Libraries were subjected to exome capture and sequenced in multiplexed reactions. Bioinformatics pipeline for sequencing reads processing, mapping, and genotype calling. *IWGSC CSS reference supplemented with a de novo assembly of unmapped reads from Kronos (Krasileva et al. 2017). (Color figure online)