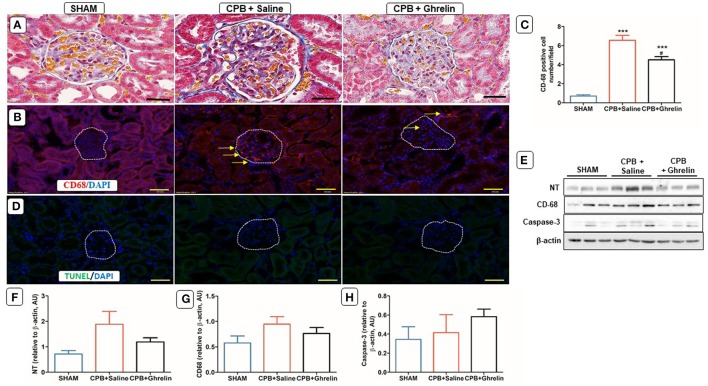
Figure 7.
Ghrelin treatment improved renal inflammation, but not apoptosis in rats following CPB. (A) Azan-Mallory stained kidney section of a sham rat showing a normal glomerular membrane, capsular and tubular capillaries; a CPB rat showing the presence of collagen accumulations (blue staining) surrounding the tubules, inflammatory cell infiltration within the glomerulus and increased capsular space; a ghrelin treated rat showing reduced cell infiltration and capsular space (40x). (B) Immunofluorescence staining was used to access the levels of renal cortical CD-68 (red stain; yellow arrows) positively-stained cells. (C) Quantitative measurement of CD-68 positive cell per 20 fields. (D) In situ TUNEL-assay showed the absence of apoptotic cells (green stain) in the glomeruli. Nuclei were labeled with 4', 6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI, blue). The merged image is presented in this figure. In all images scale bar is 50 μm. (E) Protein expression levels of NT, CD-68 and caspase-3 detected by Western blotting. β-actin was used as an internal control. (F–H) Bar graph showing the densitometric analysis of the NT, CD-68 and caspase-3 Western blots. The data shown are the mean ± SEM; N = 3 rats per group. Data were analyzed by a one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's post hoc test. ***p < 0.001 vs. sham group; #p < 0.05 vs. CPB saline group.