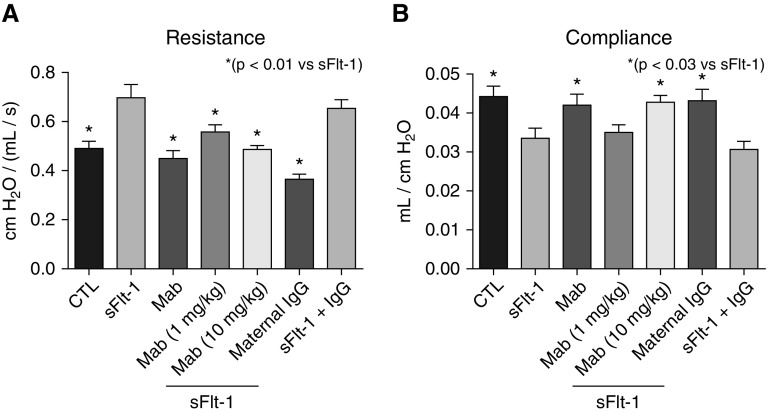
Figure 4.
Effects of intraamniotic (i.a.) sFlt-1 (soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase 1) exposure and uterine artery monoclonal antibody (mAb) treatment on lung function as assessed on 14-day-old rats. (A) Intraamniotic exposure to sFlt-1 increased infant lung resistance, which was improved with maternal mAb therapy. (B) Similarly, i.a. exposure to sFlt-1 decreased lung compliance, which was increased in rats treated by maternal mAb infusion before birth. As shown, treatment with nonspecific IgG did not affect lung resistance or compliance in control (CTL) or sFlt-1–exposed pups. Error bars show SEM. Numbers of pups studied in each group are: CTL, n = 32; sFlt-1, n = 23; mAb alone, n = 10; sFlt-1 + mAb (1 mg/kg), n = 19; sFlt-1 + mAb (10 mg/kg), maternal IgG, n = 15; sFlt-1 + IgG, n = 12.