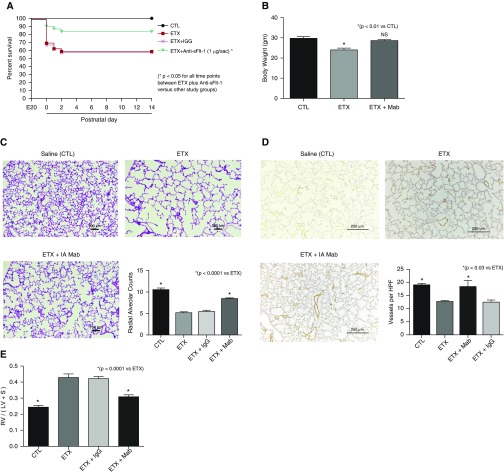
Figure 8.
Effects of prenatal intraamniotic (i.a.) monoclonal antibody (mAb) treatment on lung structure and right ventricular hypertrophy (RVH) after i.a. endotoxin (ETX) exposure. (A) In comparison with control rats (CTL), i.a. exposure to ETX reduced survival in rat pups after birth, and neonatal survival was improved by antenatal mAb treatment. Numbers of pups studied for the survival aim included 30 fetuses for the groups receiving either saline, ETX alone, or ETX plus mAb, and 20 fetuses for the ETX plus IgG groups. *P < 0.05 at each time point for comparisons between ETX plus mAb versus each of the other study groups. (B–E) Antenatal mAb therapy improved body weight (B), distal lung growth (C), and vessel density (D), and improved RVH (E). As shown, i.a. treatment with nonspecific IgG did not affect lung structure or RVH. Scale bars: (C) 100 μm; (D) 250 μm. Error bars show SEM. Numbers of each group for panels B–E are: CTL, n = 11; ETX, n = 10; ETX + mAb, n = 10; ETX + IgG, n = 10. HPF = high-power field; LV = left ventricle; NS = not significant; RV = right ventricle; S = septum; sFlt-1 = soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase 1.