Figure 3.
RGC Axon-Axon Interactions Require CYFIP2 Function
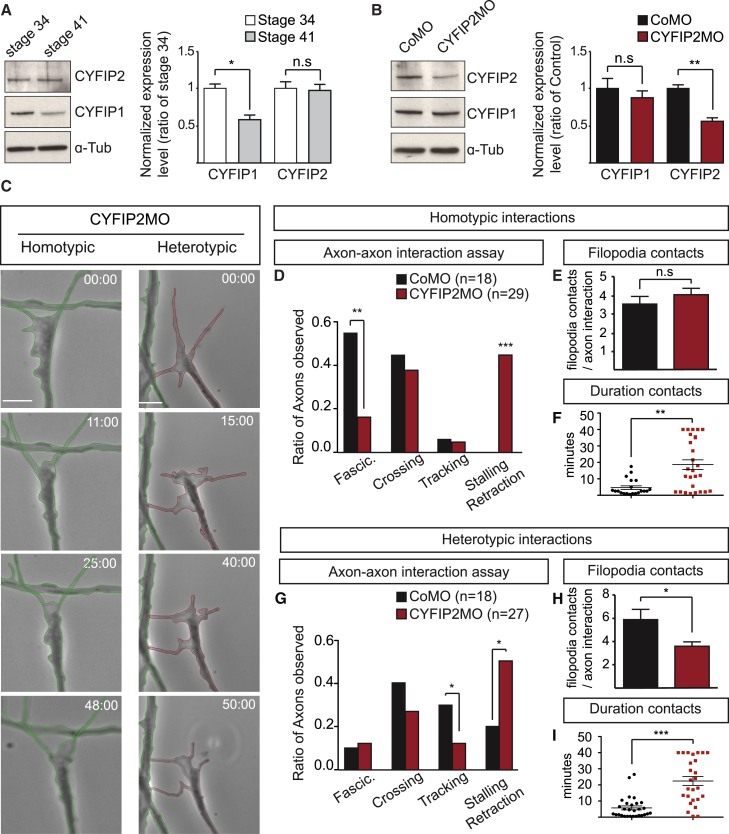
(A) Representative western blots and quantification of CYFIP1 and CYFIP2 levels in Xenopus eye lysates at stages 34 and 41 (n = 3, normalized to α-Tubulin).
(B) Representative western blots and quantification of CYFIP2 (n = 6, normalized to α-Tubulin) and CYFIP1 (n = 3, normalized to α-Tubulin) levels in CYFIP2MO- compared to CoMO-injected embryos at stage 34.
(C) Examples of stalling growth cones (GCs) during homotypic and heterotypic responses after CYFIP2 depletion.
(D) Quantification of the homotypic interaction responses after CYFIP2 knockdown.
(E and F) Quantification of the number (E) and duration (F) of filopodia contacts during fasciculation and stalling events in CYFIP2MO (n = 7 GC, n = 27 filopodia) compared to CoMO (n = 6 GC, n = 20 filopodia) conditions for homotypic interactions.
(G) Quantification of the heterotypic interaction responses after CYFIP2 knockdown.
(H and I) Quantification of the number (H) and duration (I) of filopodia contacts during tracking and stalling events in CYFIP2MO (n = 8 GC, n = 26 filopodia) compared to CoMO (n = 5 GC, n = 29 filopodia) conditions for heterotypic interactions.
(D and G) Numbers of events analyzed are indicated on the graph (n = 12 independent experiments).
(E–I) Error bars represent SEM. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, n.s., non-significant (Mann-Whitney test for A, B, E, F, H and I) and (Fisher’s exact test for D and G). Time stamps are in the format of min:s. Scale bars: 5 μm (C).