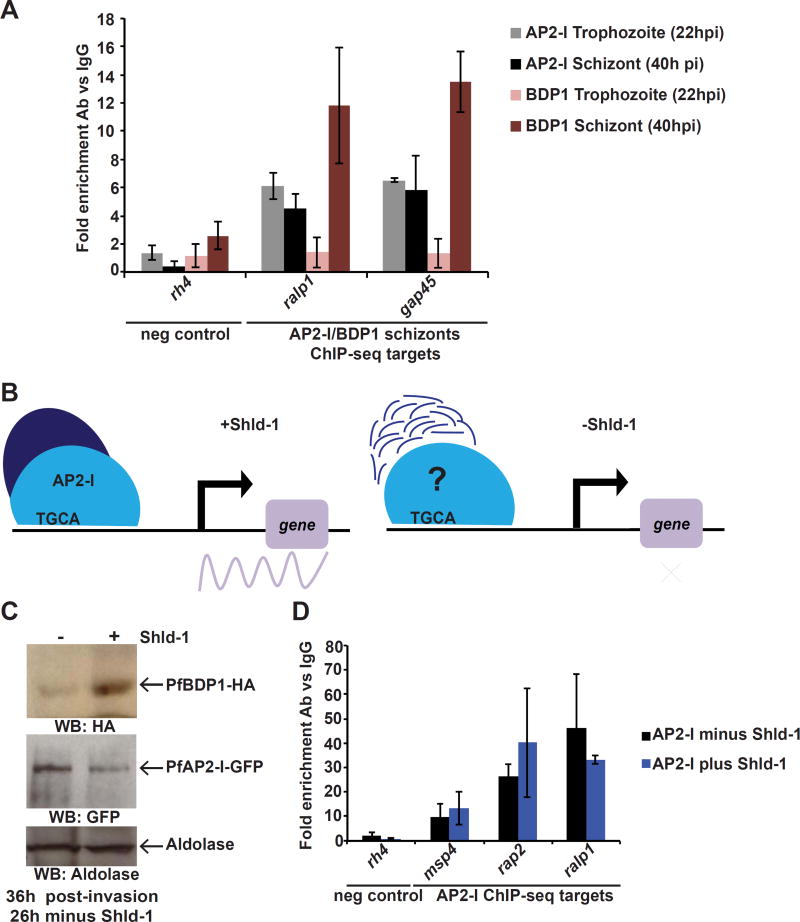
Figure 7. PfAP2-I binding precedes PfBDP1 binding to the target gene promoters.
A- ChIP-qPCR demonstrates that PfAP2-I-GFP, but not PfBDP1-HA, is already bound to its target promoters at 22hpi. Data are represented as mean ± SD and n=2. The schizont data is the same as in Figure S6B (For PfBDP1 ChIP positive control see Figure S7A). B- In the presence of Shld-1, there are wildtype levels of PfBDP1, but in the absence of Shld-1, PfBDP1-DD is degraded and target gene transcription cannot be initiated (Josling et al., 2015). PfAP2-I may or may not remain associated to the TGCA DNA motif in the absence of PfBDP1. C- ChIP-qPCR shows that in PfAP2-I-GFP::PfBDP1-HA-DD parasites (see Figure S7), PfAP2-I-GFP remains bound to the target gene promoters even when PfBDP1 is knocked down (- Shld-1). Data are represented as mean ± SD and n=3. rh4 was used as negative control for DNA-binding.