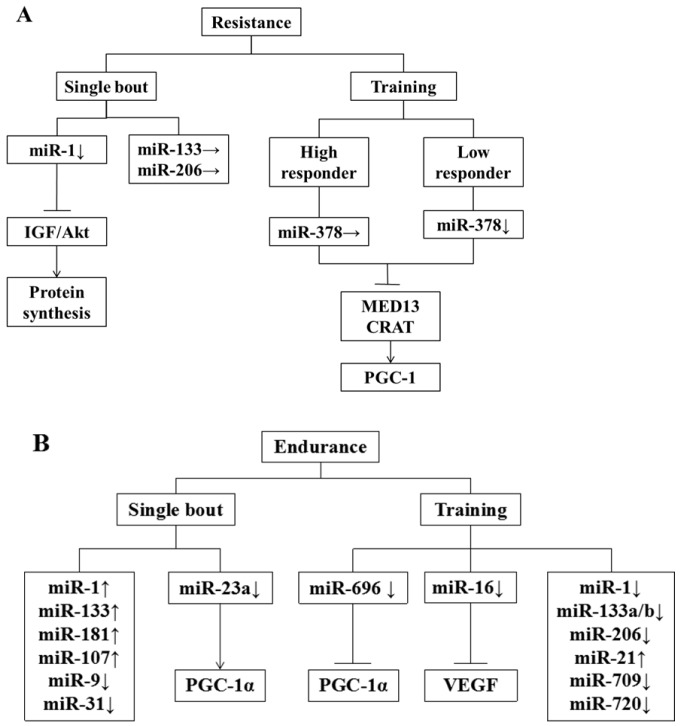
Figure 1.
Effect of exercise on miRNAs. (A) A single bout of resistance exercise in men reduces miR-1 expression and does not affect the expression of miR-133a and -206. The miR-1 can promote protein synthesis through the IGF-1/Akt signal pathway. The change in the expression of miR-378 is positively correlated with the improved quality of skeletal muscle due to resistance exercise. Similarly, miR-378 inhibits PGC-1β-mediated mitochondrial metabolic effects by MED13 and CRAT; (B) a single bout of endurance exercise in mice reduces the expression of miR-23a and increases the expression of miR-1, -181 and -107. Endurance training increases the expression of miR-21 and decreases the expression of miR-696, -709 and -720 in mice. ↑ increased; ↓ decreased; → unchanged; ⊥ inhibited. IGF: insulin-like growth factor; Akt: protein kinase B; PGC-1: peroxisome proliferation-activated receptor-γ coactivator-1; MED13: mediator complex subunit 13; CRAT: carnitine acetyltransferase; VEGF: vascular endothelial growth factor.