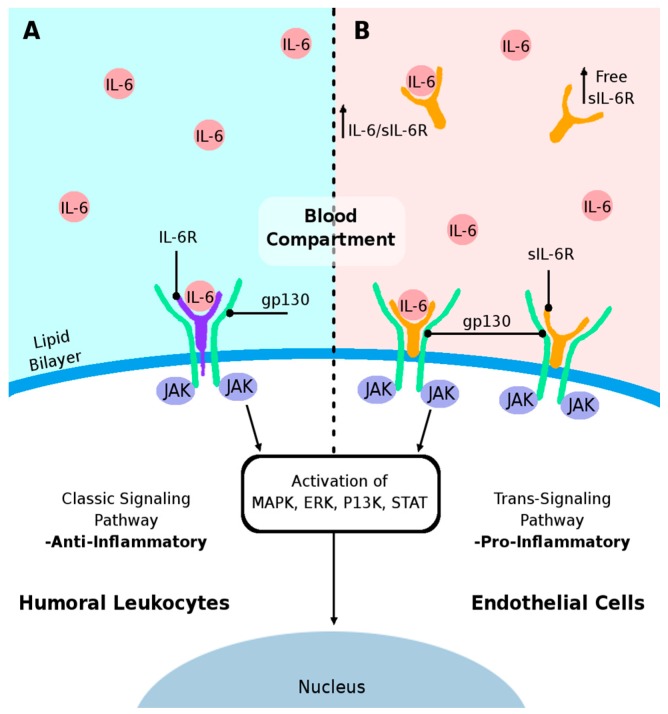
Figure 3.
Schematic diagram proposed mechanism of humoral IL-6-mediated inflammation in triggering EC damage. (A) The IL-6 cytokine is an important anti-inflammatory protein for regulation of cell survival by binding to the cell membrane receptor IL-6R/gp130 complex leading to activation of JAK, subsequent activation of other signal transduction molecules which influences nuclear gene transcription (down arrow) via the classic signaling pathway; (B) Excessive sIL-6R (up arrow) in the blood, resultant of cleavage from the membrane (shedding) or de novo synthesis, could bind to excess IL-6 and form IL-6/sIL-6R/gp130 complex on ECs. This complex formation on the EC membrane would result in the activation of signal transduction kinases and induce a pro-inflammatory response by activating the trans-signaling pathway.