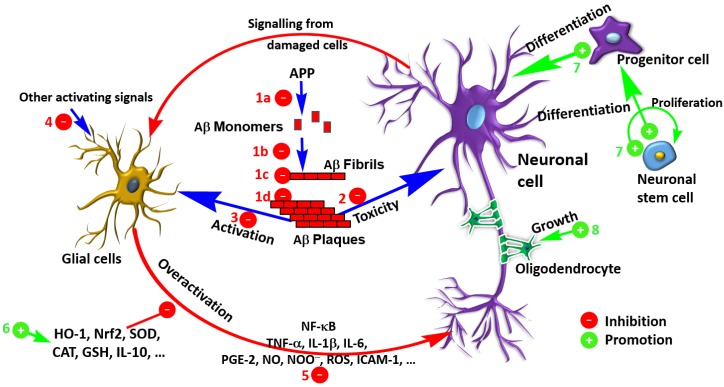
Figure 5.
Overview of the therapeutic potential of salvianolic acids and RA derivatives in dementia via the various mechanisms of Aβ pathology. Mechanisms include inhibition of Aβ formation (1a), fibril formation/elongation (1b), interaction with fibrils (1c) and aggregated plaques (1d), toxicity in neuronal cells (2) and glial activation (3). The activation of glial cells to initiate inflammatory cascades (5) by various agents including other toxicants such as ROS (4) could be inhibited through processes including induction of antioxidant defenses (6). Other established mechanisms are neuronal regeneration from stem cells (7) and axonal and myelin sheath protection (8).