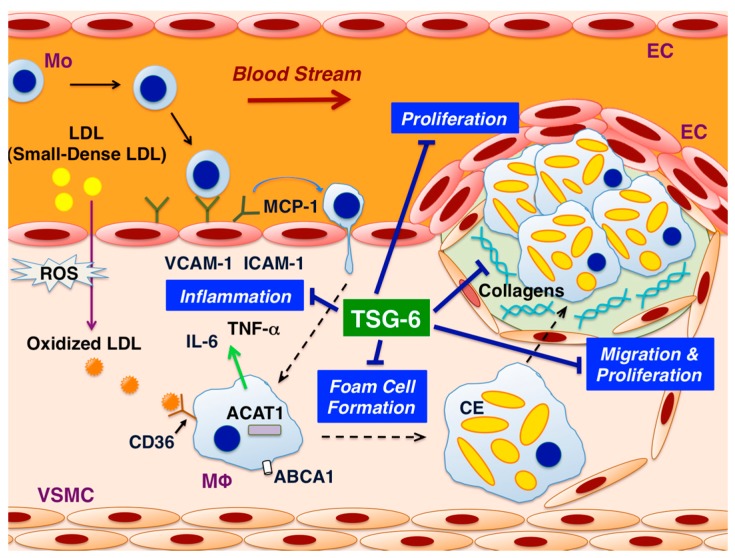
Figure 1.
Mechanisms underlying the atheroprotective effects of tumor necrosis factor-stimulated gene-6 (TSG-6). This figure illustrates the suppressive effects of TSG-6 on atherosclerotic plaque formation in the arterial wall. TSG-6 prevents atherosclerosis by suppressing the inflammatory responses in endothelial cells (ECs) and macrophages, oxidized low-density lipoprotein (LDL)-induced foam cell formation in macrophages, and the migration and proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs). TSG-6 increases the production of collagen-1 and -3 by VSMCs. Abbreviations: ACAT1 = acyl-coenzyme A:cholesterol acyltransferase-1; ABCA1 = ATP-binding cassette transporter A1; CE = cholesterol ester; ICAM-1 = intercellular adhesion molecule-1; MCP-1 = monocyte chemotactic protein-1; Mo = monocyte; MΦ = macrophage; ROS = reactive oxygen species; VCAM-1 = vascular cell adhesion molecule-1.