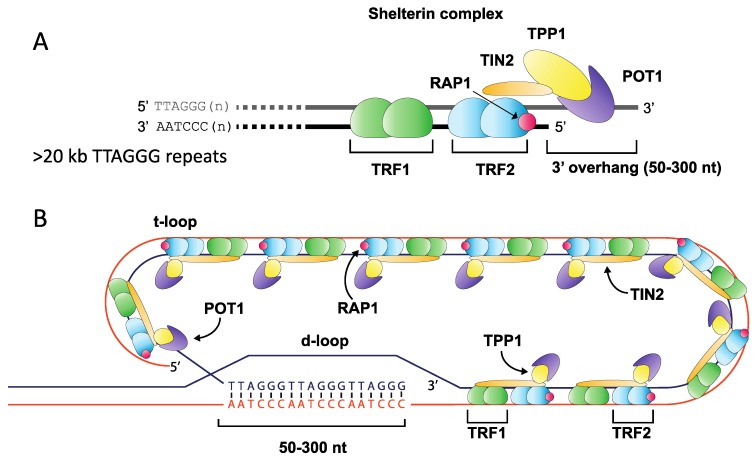
Figure 1.
Overview of telomere structure. The terminal ends of mammalian chromosomes consist of an array of (TTAGGG)n repeats ending with a 3′ overhang of between 50 and 300 nt in length (A). This array is bound by many protein components including members of the shelterin complex, which anchors to the repeat array through Telomere Repeat binding Factors 1 & 2 (TRF1 and TRF2), binding repeats as a homodimer, and forming a complex with TIN2 (TRF1-interacting factor), RAP1 (Repressor Activator Protein 1), TPP1 and POT1 (Protection of Telomere 1) (A). The repeat array folds into a higher-order t-loop structure where the 3′ overhang displaces a portion of the forward strand to create a d-loop, thereby sequestering the free chromosome end from the DNA repair machinery (B).