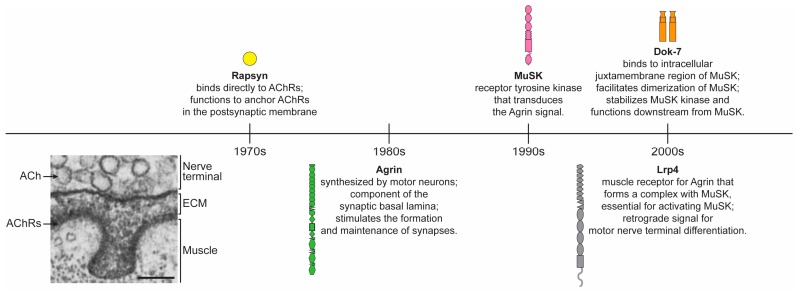
Figure 1.
Timeline for the discovery of key molecular players at the neuromuscular synapse. The peripheral membrane protein Rapsyn binds to the intracellular region of AChRs and anchors AChRs and other muscle proteins in the postsynaptic membrane. Later studies identified Agrin as a critical motor neuron-derived signal that is deposited into the synaptic lamina and stimulates the formation and maintenance of neuromuscular synapses, including the clustering of AChRs. Shortly thereafter, MuSK was identified, shown to mediate the response to Agrin, and found to be critical for both postsynaptic and presynaptic differentiation. More than a decade elapsed before the Agrin receptor was identified as Lrp4. Lrp4 functions not only to bind Agrin, promoting association between Lrp4 and MuSK and stimulating muscle differentiation, but also acts in turn as a retrograde signal for presynaptic differentiation. During this same time period, Dok-7 was identified and found to bind to tyrosine phosphorylated MuSK, stabilize MuSK in an active tyrosine-phosphorylated state and function downstream from MuSK. ACh, Acetylcholine. AChRs, Acetylcholine Receptors. ECM, Extracellular matrix. MuSK, muscle specific kinase. Lrp4, LDL receptor related protein 4. Dok-7, docking protein 7. Bar, 100 nm.