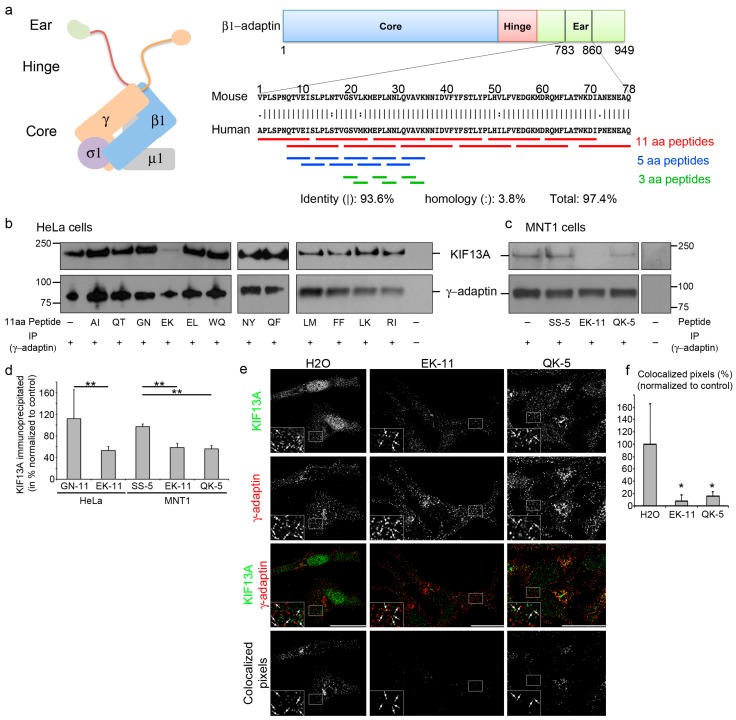
Figure 1.
Adaptor protein (AP)-1-derived peptides disrupt the AP1–KIF13A interaction. (a) Diagram showing AP-1 complex and β1-adaptin with core (blue), hinge (red), and ear (green) domains, KIF13A binding mouse and human sequences, and corresponding peptides (11aa (red), 5aa (blue), 3aa (green)); (b,c) Western blot of γ-adaptin immunoprecipitations of HeLa (b) and MNT-1 (c) cell lysates incubated or not with 1 µg of peptide using KIF13A (top) or γ-adaptin (bottom) antibodies; (d) Quantification of KIF13A revealed γ-adaptin immunoprecipitates; (e) Immunofluorescence on MNT-1 cells treated with EK-11, QK-5 or H2O as control using KIF13A (1st lane, green) and γ-adaptin antibodies (2nd lane, red). Individual and merged (3rd lane) channels are shown. Co-localization masks (4th lane) showing overlapped pixels (arrows in magnified insets of the boxed area); (f) Quantification of co-localized γ-adaptin/KIF13A pixels (excluding nuclei and Golgi area). Data are the average normalized to control and presented as a mean ± standard deviation. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01. Bars, 10 µm.