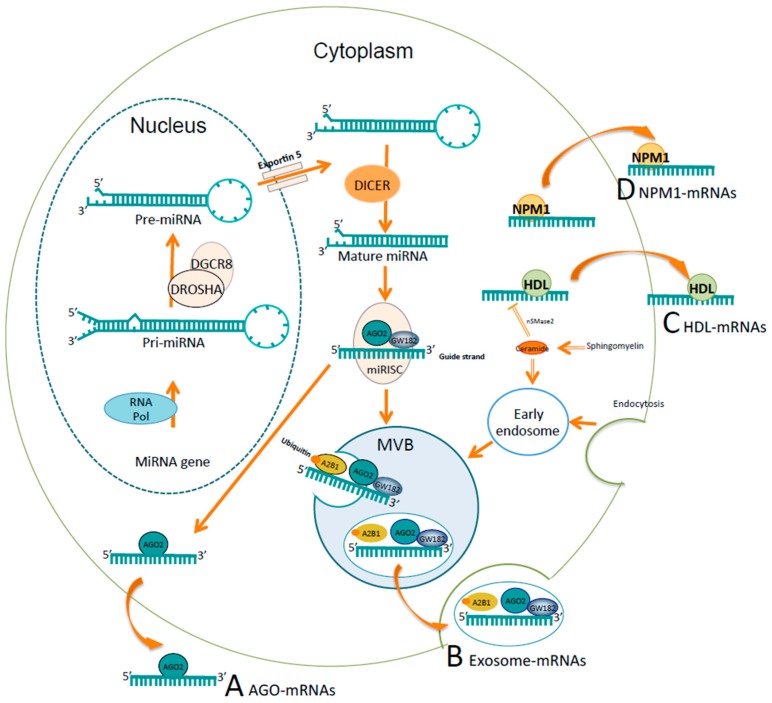
Figure 2.
Mechanisms of secretion of miRNAs. (A) Secretion of the miRNAs associated with Argonaute2 protein (AGO2); (B) Secretion of the miRNAs by exosomes; (C) Secretion of the miRNAs associated with high-density lipoprotein (HDL); (D) Secretion of the miRNAs associated with the RNA binding protein nucleophosmin (NPM1). (A) miRNAs associated with AGO2, a main component of the RISC, can be stably exported into plasma samples. (B) miRNAs are sorted into multivesicular bodies (MVBs) derived from early endosomes. This mechanism requires ceramide production on the cytosolic side by neutral sphingomyelinase 2 (nSMase2), ESCRT machinery, and sumoylated hnRNPA2B1 protein, which specifically binds mature miRNAs and controls their loading into MVBs. MVBs are enriched with GW182 and AGO2, which are known to regulate the function of miRNAs. MVBs fuse with the plasma membrane and release exosomes into the extracellular medium. (C) miRNAs bound to HDL also can be stably exported into plasma samples via a mechanism repressed by nSMase2. (D) NPM1 binds miRNAs from the culture supernatants of tumor cell lines and fibroblasts while protecting them from RNase activity.