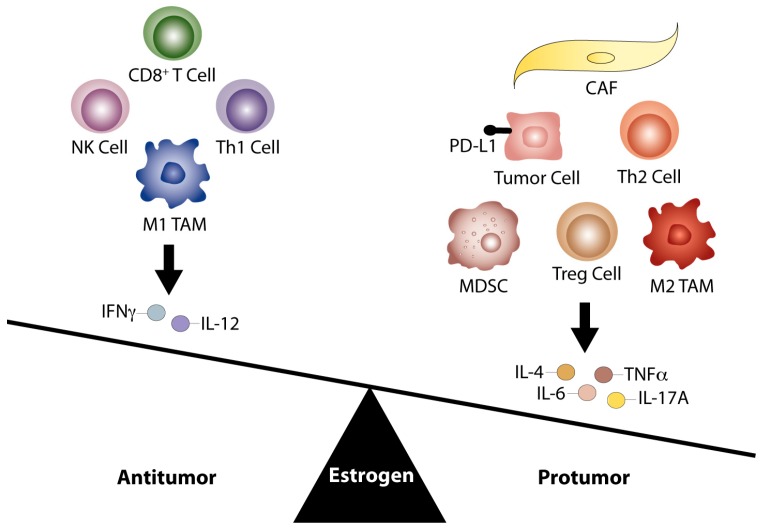
Figure 1.
The E2 pathway promotes a protumor TME. The E2 pathway contributes to aberrant regulation of antitumor immunity, enhancing a greater number of protumoral responses within the TME. Current literature suggests E2 may facilitate an immunosuppressive TME by shifting the balance in favor of Th2 responses, production of tumor-promoting cytokines (IL-6, IL-4, TNFα, and IL-17A), and M2 TAM infiltration compared to Th1 responses, associated Th1 cytokines (IL-12 and IFNγ), and M1 TAM infiltration. E2 may further promote tumor immune evasion through proliferation of Treg and MDSC populations, increased tumor cell PD-L1 expression, and inhibition of CD8+ T cell and NK cell induced apoptosis. CAFs may additionally support a protumor environment by supplying paracrine sources of E2 and IL-6. Therefore, targeted inhibition of the E2 pathway may act as a novel strategy to enhance the effects of immunotherapies and reverse this immune imbalance within the TME.