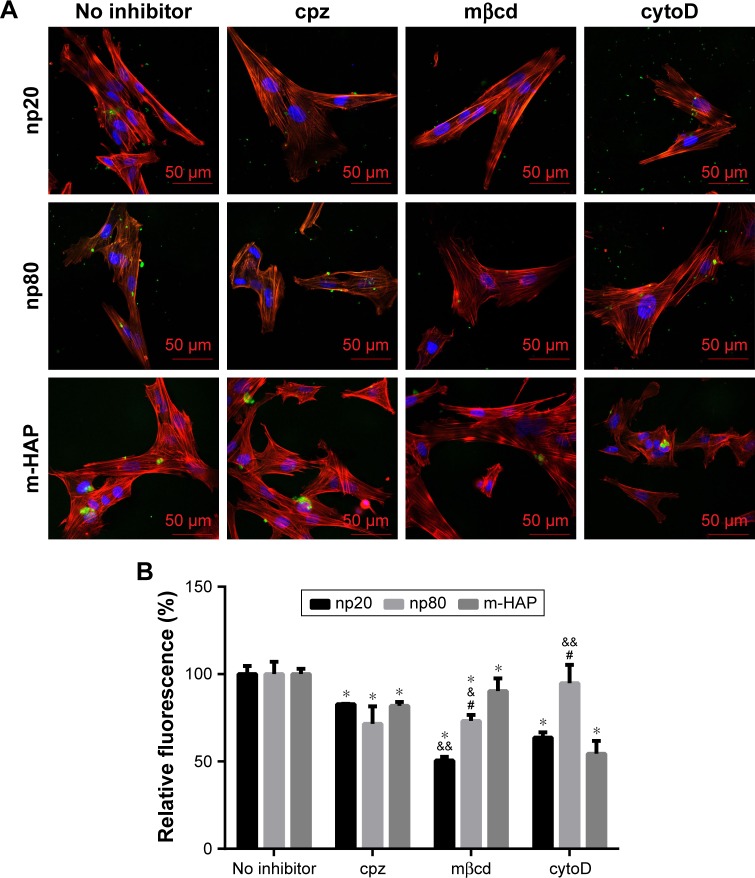
Figure 7.
The role of different endocytic pathways in HAPs uptake in hWJ-MSCs. Cells were exposed to HAPs with or without cpz, mβcd, and cytoD, respectively. (A) CLSM images of hWJ-MSCs exposed to HAPs for 2 h. Cells stained for nuclei (blue) and actin (red). HAPs are shown in green color. Scale bars: 50 μm. (B) Quantification of HAPs uptake after hWJ-MSCs were treated with HAPs for 2 h. *P<0.01 versus no inhibitor control, &P<0.05; &&P<0.01 versus m-HAP group, #P<0.01 versus np20 group.
Abbreviations: HAPs, hydroxyapatite particles; hWJ-MSCs, human umbilical cord Wharton’s jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells; cpz, chlorpromazine; mβcd, methyl-β-cyclodextrin; cytoD, cytochalasin D; CLSM, confocal laser scanning microscopy; np20, hydroxyapatite nanoparticles 20 nm in diameter; np80, hydroxyapatite nanoparticles 80 nm in diameter; m-HAP, micro-sized HAP particles; HAP, hydroxyapatite.