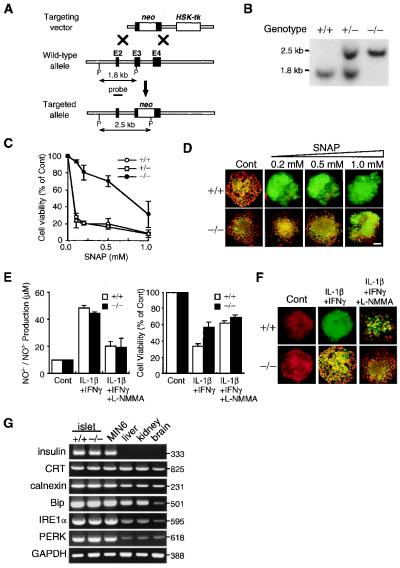
Figure 6.
Cells lacking CHOP are resistant to NO-mediated apoptosis. (A) Strategy used to disrupt the CHOP gene. (B) Southern blot of PstI-digested genomic DNA generating a 1.8-kb fragment (wild type) and a 2.5-kb fragment (mutant). (C) Effects of SNAP on cell viability of CHOP+/+ and CHOP−/− islets. Ten medium-sized isolated islets in each group were treated with SNAP for 48 h (mean ± SE, n = 3). (D) Effects of SNAP on mitochondrial depolarization in CHOP+/+ and CHOP−/− islets. Islets were stained with DePsipher 48 h after treatment with SNAP. The red fluorescence represents intact mitochondrial potential, and the green fluorescence represents disrupted potential. [Original magnification, ×400 (bar = 20 μm).] (E) NO production and cell viability of CHOP+/+ and CHOP−/− islets 48 h after treatment with cytokines or cytokines + NG-monomethyl-l-arginine (5 μM) (mean ± SE, n = 3). (F) Effects of cytokines on mitochondrial depolarization in CHOP+/+ and CHOP−/− islets. Islets were stained with DePsipher 48 h after treatment with cytokines. (G) Reverse transcription–PCR of mRNAs for ER proteins and ER stress transducer proteins in CHOP+/+ and CHOP−/− islets, MIN6 cells, and mouse tissues.