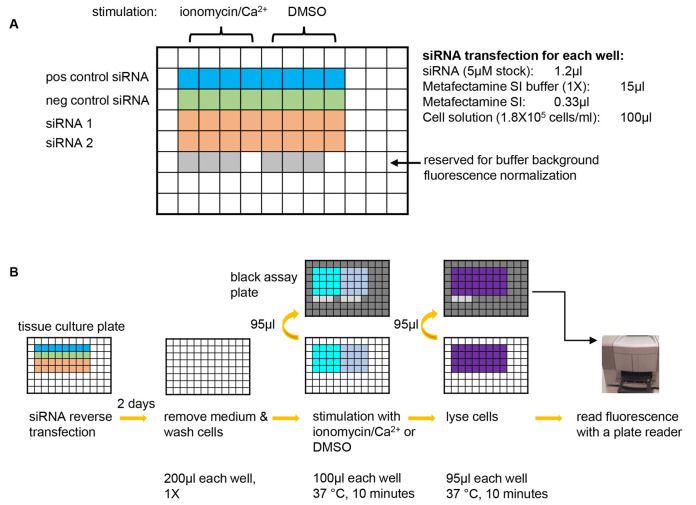
Figure 1. A graphic summary of the NPY-Venus secretion assay.
A. Plate design for an example experiment of testing two siRNAs of interest. A positive control siRNA that is known to inhibit NPY-Venus secretion (e.g., CADPS siRNA) and a negative control siRNA that is known not to affect NPY-venus secretion (e.g., Dharmacon non-targeting siRNA D-001210-03-20) should always be included in each experiment. 8 wells are used for each siRNA with 4 wells for stimulation with ionomycin/Ca2+ and the other 4 for background secretion. 6 wells are left blank so that the same wells on the black assay plates (see B) can be used for determining the background fluorescence of plain buffer. pos control siRNA: positive control siRNA; neg control siRNA: negative control siRNA. B. Steps of the NPY-Venus secretion assay. From left to right: conduct reverse transfection with siRNAs; after two days of incubation, remove culture medium and wash cells with pre-warmed PSS-Na; stimulate cells with PSS-Na containing either ionomycin or DMSO and then transfer the supernatant to a black assay plate; lyse cells with 1% Triton X-100 and then transfer to a black assay plate; add plain buffer to the reserved wells (see A) and then determine NPY-Venus fluorescence with a plate reader. Refer to texts for details.