Fig. 5.
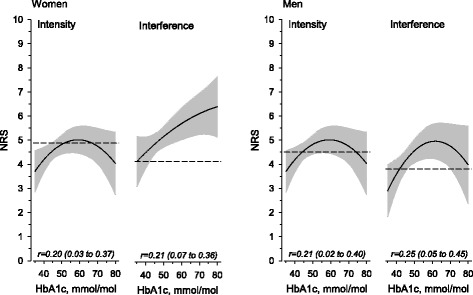
Relationships between HbA1c and intensity and interference of pain among women and men with diabetes. The curves were derived from regression models including quadratic term of HbA1c. The curves were adjusted for age, physical activity, depressive symptoms, alcohol use, smoking and number of comorbidities. The grey area represents 95% confidence intervals. Dotted lines show means of subjects without diabetes. Adjusted curvilinear correlation was used. All curvilinear correlations were significant
